
Schermerhorn coat of arms. (Frontispiece, Richard Schermerhorn Jr., Schermerhorn Genealogy and Family Chronicles, 1914.)

Schermerhorn’s original $300 mortgage to Morgan, dated May 27, 1809, as recorded by the Middlesex County Clerk’s Office, New Brunswick, New Jersey, and prominently witnessed by Judge Jacob Van Wickle’s daughters. Judge Van Wickle was a principal in the Old Bridge, New Jersey, pottery concern in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, and also owned land on the southwest end of Old Bridge, near Schermerhorn’s newly acquired property.
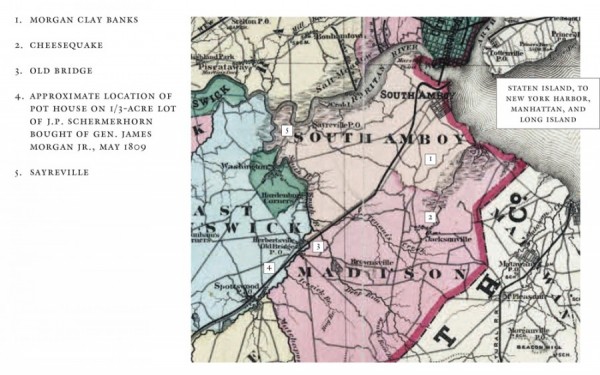
Hand-colored lithographed map, F. W. Beers and Co., 3, 1872. The pottery towns in the Middlesex County area (South Amboy, Old Bridge, Cheesequake, and Sayreville [Roundabout]) are shown here, along with the likely location of the pot house and land that John Schermerhorn bought an interest in from James Morgan Jr. in May 1809.
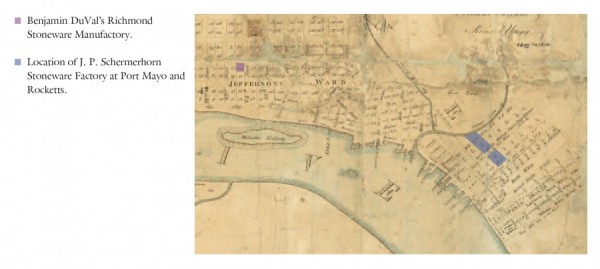
Detail, A Plan of the City of Richmond, Richard Young, 1809–1810. (Courtesy, Library of Virginia.) This plan shows the proximity of the DuVal and Schermerhorn stoneware manufactories to Rocketts Landing and the James River.

Notice, The Daily Compiler (Richmond), July 9, 1814. The sarcastic wording in this newspaper clipping reveals John P. Schermerhorn’s offended reaction to an advertisement placed by Benjamin DuVal that apparently affronted (and perhaps dishonored) him.

Advertisement placed by John P. Schermerhorn, Richmond Commercial Compiler, October 3, 1820, p. 3, col. 3.
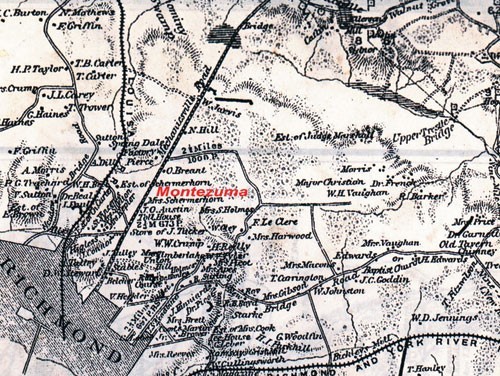
Extended view of the J. P. Schermerhorn Stoneware Factory at Rocketts, as well as Montezuma, his nearby residence in Fairfield. The view is from a map made in the 1860s (George B. Davis et al., The Official Military Atlas of the Civil War [Avenel, N.J.: Gramercy Books, 1983], pl. XIX, no. 1) and shows the Fairfield vicinity of Henrico County where Schermerhorn built his home and its proximity to his James River factory at Rocketts.

Contemporary photograph of the Georgian revival edifice rebuilt in 1910 on the same site of John P. Schermerhorn’s Montezuma. (Photo, W. Sterling Schermerhorn.) The original structure followed the same plan as this house on the Mechanicsville Turnpike just northeast of Richmond.

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Courtesy, Old Salem, Inc., Collection of the Museum of Early Southern Decorative Arts; photo, MESDA.) This ovoid storage jar, decorated with brushed-cobalt floral motifs involving horizontal vines interspersed with alternating round blossoms, is stamped with Schermerhorn’s maker’s mark, which includes a leaflike flourish.

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 17 1/2". Mark, below handles: “5.” Capacity: 5 gallons. (Private collection; unless otherwise noted, all photos by Gavin Ashworth.) This large, ovoid storage jar is stamped with a vivid maker’s mark and, with its brushed-cobalt floral motifs of horizontally flowing vines interspersed with round blossoms, is one of the most significant signed surviving vessels made by Schermerhorn.

Detail of the stamped maker’s mark with stamped cartouches on the vessel illustrated in fig. 9. (Old Salem, Inc., Collection of the Museum of Early Southern Decorative Arts; photo, MESDA.)

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) This monumental storage jar displays the characteristic Schermerhorn rounded rim, well-defined collar/neck, and extruded crescent-shaped handles brushed with blue cobalt and placed high on the shoulder. Centered on one side is an incised federal-style eagle filled with blue cobalt. On the reverse are floral vines separating two rounded blossoms.
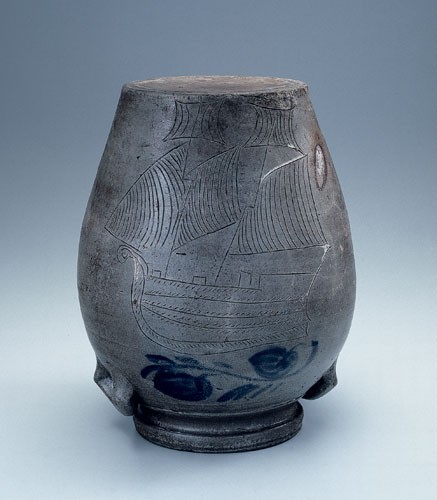

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) Shown upside down, this ovoid storage jar is embellished with a blue floral vine, which connects leaves opposite opposing rounded flowers along the shoulder, as well as an inverted incised ship.

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) The incised and cobalt-decorated long-legged bird on this ovoid storage jar appears to be nibbling on a cobalt flower with cobalt festoons above. The reverse is decorated with the most common motif used by Schermerhorn, opposing floral blossoms separated by flowing vines.

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15". Mark, below rim: stamped “5.” Capacity: 5 gallons. (Private collection.) This ovoid vessel displays a well-defined incised and cobalt-filled rooster, or game cock, standing on horizontal cobalt festoons similar to those above the bird illustrated in fig. 14.
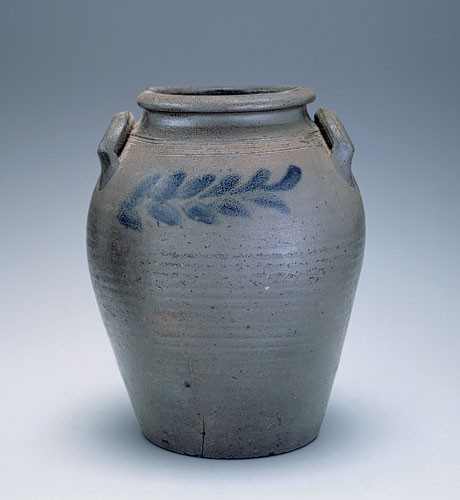

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 3/4". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) A simple, brushed, blue-cobalt horizontal vine decorates both sides of this robust ovoid jar with pronounced neck, rounded rim, and highly placed extruded crescent-shaped handles.
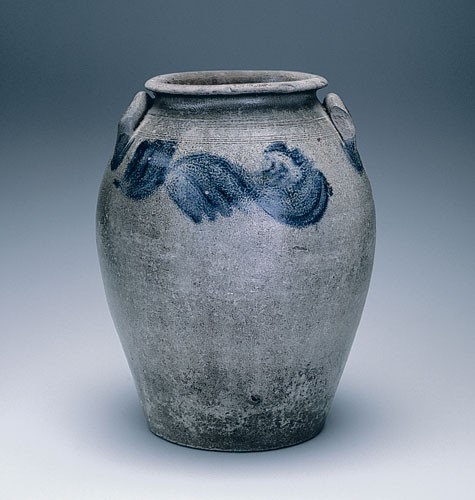

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/4". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)
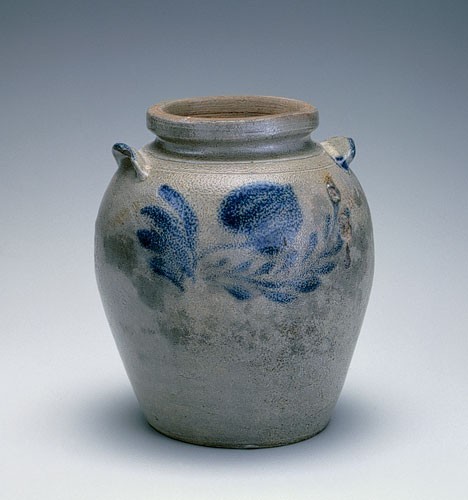

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 9 1/8". Capacity: 1 gallon. (Private collection.)
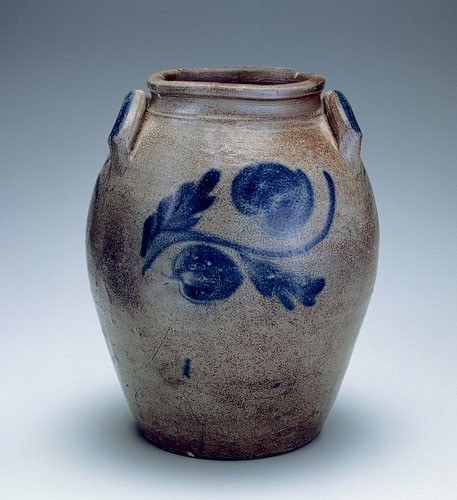

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 11 3/4". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.)
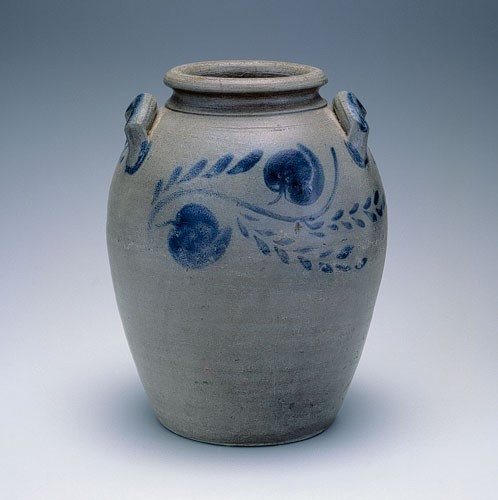

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) An excellent example of Schermerhorn’s early Richmond production, this thick-walled, well-formed ovoid vessel has a pronounced rounded rim, highly placed crescent-shaped handles brushed with cobalt, and horizontal vines and two prominent round floral blossoms.
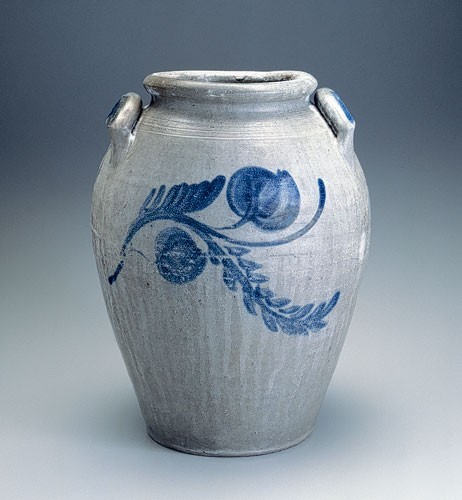

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 3/4". Mark, beneath each handle: “3.” (Private collection.)
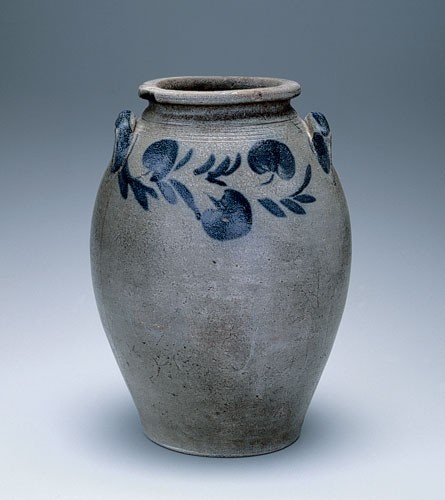

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/4". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)
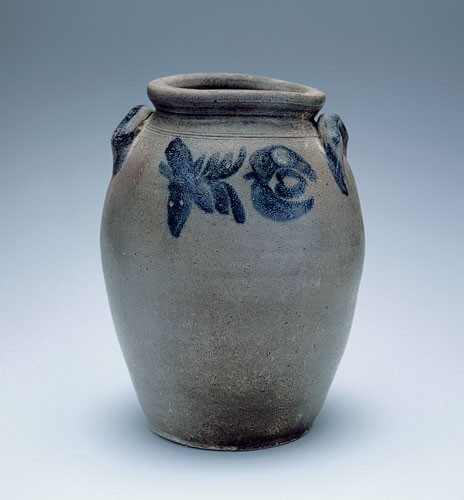

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.)
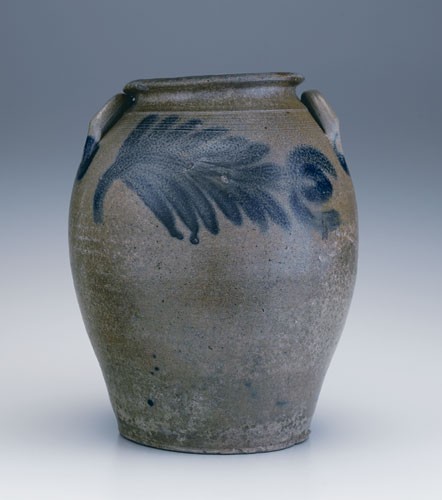

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Kurt C. Russ.) This ovoid stoneware vessel with its pronounced rounded rim and applied crescent handles exhibits a bold brushed-cobalt open-petaled flower oriented horizontally and extending from a large cluster of cobalt leaves. In underglaze cobalt lettering on its base is written “Shafter Edward Drinkard.”

Detail of the inscription on the base of the storage jar illustrated in fig. 25.
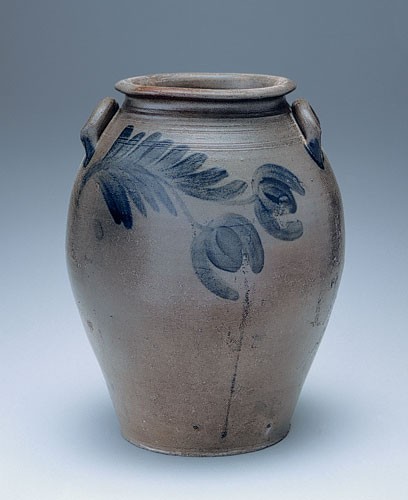

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.) This ovoid storage jar is decorated on one side with a brushed-cobalt profile of a man—perhaps a “man-in-the-moon”—and, on the other side, an underscored capacity mark (“2”).

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 10". Capacity: 1 gallon. (Private collection.) Embellished on the front of this ovoid storage jar is a primitive cobalt slip–decorated eagle with extended wings, a shielded chest, and talons holding, respectively, an olive branch and an arrow. On the reverse is a similar eagle, with an olive branch in both talons.
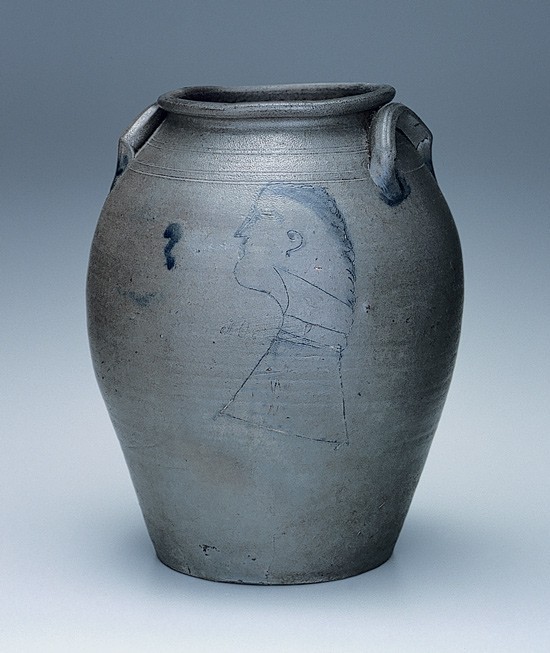

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.) On one side of this large, elongated vessel is a cobalt capacity mark—“4”—elaborately underscored with horizontal blue lines and squiggle mark. On the other side is an incised profile of a man highlighted with blue, and, incised across the figure’s collar, is “john p.” The image is presumed to be the signed self-portrait of the vessel’s maker, John P. Schermerhorn.
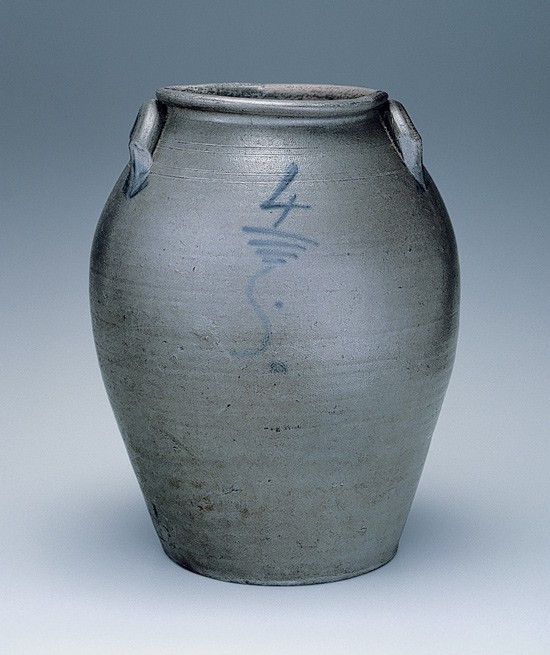

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.) On one side of this large, elongated vessel is a cobalt capacity mark—“4”—elaborately underscored with horizontal blue lines and squiggle mark. On the other side is an incised profile of a man highlighted with blue, and, incised across the figure’s collar, is “john p.” The image is presumed to be the signed self-portrait of the vessel’s maker, John P. Schermerhorn.
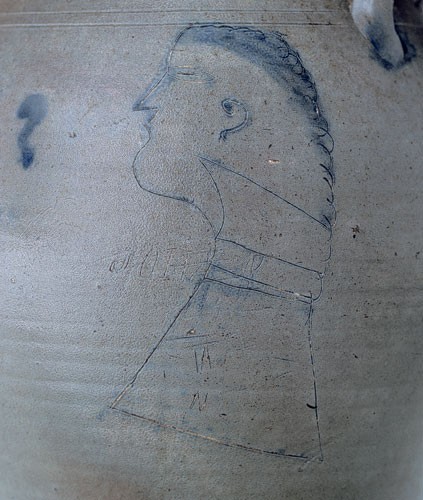

Detail of the incised profile depicted on the jar illustrated in fig. 30

Storage jars, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. From left to right: H. 9 1/2" (1 gallon), 11 1/2" (1 1/2 gallon), 12 1/2" (2 gallons), 13 3/4" (3 gallons), and 15" (4 gallons). (Private collection.) The squiggly cobalt mark found beneath the capacity mark in each of the vessels of this graduated series could represent a J or an S; hence, the potter’s signature is left to interpretation.

Storage jar, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) A brushed cobalt date (“1837”) appears on the side of this vessel; on the reverse, a characteristic capacity mark (“3”) is underscored with a horizontal line and possibly a J, with blue highlights at the terminations of both extruded crescent-shaped handles and rounded rim. The date might refer to Schermerhorn’s last year of potting in Richmond. This piece was pictured in H. E. Comstock, Pottery of the Shenandoah Valley Region (Winston-Salem, N.C.: Museum of Early Southern Decorative Arts, 1994), p. 317, fig. 6.3, where it was incorrectly attributed to Rockbridge.

Storage jars, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 11 7/8" (2 gallons); 14" (3 gallons). (Private collection.) These two important stoneware jars show the heretofore undocumented association of the horizontally oriented brushed-cobalt floral spray with undulating vines interspersed with opposing or alternating floral blossoms with the brushed blue cobalt capacity designations underscored with horizontal lines and a squiggle suggestive of (depending on the crock) either a J or an S like the one on the reverse of the incised self-portrait crock.

Jug, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 16". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)

Jug, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 17 1/2". Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.)

Pitcher, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/8". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.)

Pitcher, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 10 3/4". Capacity: 1 gallon. (Private collection.)
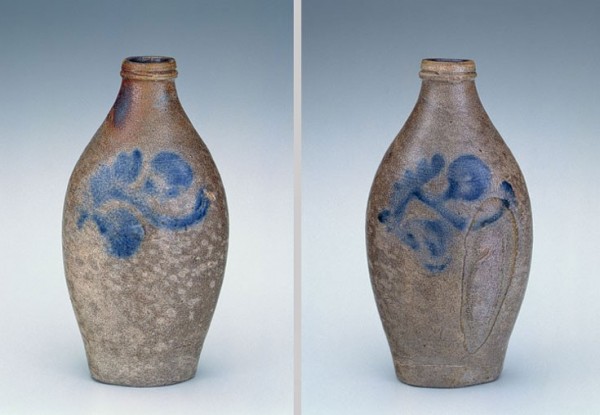

Flask, Schermerhorn Pottery, Richmond, Virginia, 1817–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 7 1/2". (Private collection.) This rather diminutive flask, with flattened sides decorated with brushed-cobalt floral vines separating opposing blossoms, has a distinctive incised ring on the lip and a concave bottom, resembling that of handmade glass bottles of the period.
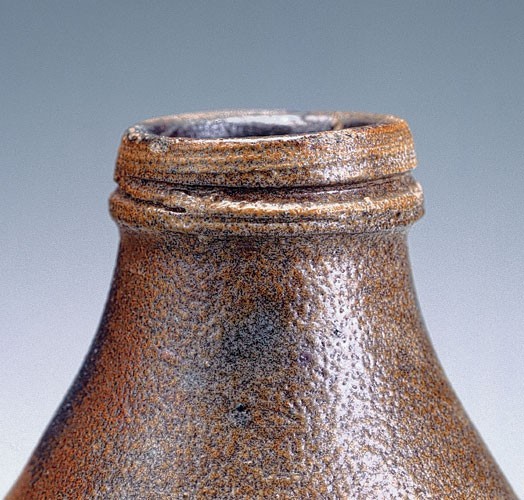

Detail of the neck of the flask illustrated in fig. 39.
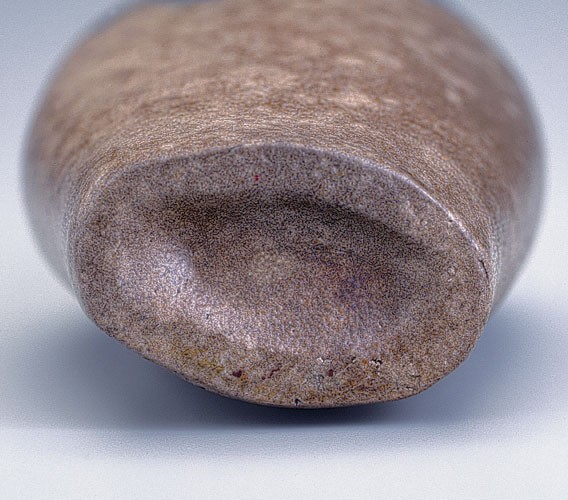

Detail of the concave bottom of the flask illustrated in fig. 39.
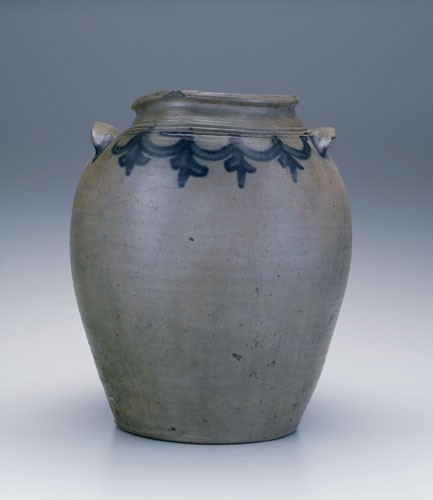

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.) This robust jar, with its diminutive, slightly rolled rim and concave neck, has on its front three incised concentric ridges at the shoulder, slightly curved earlike handles with cobalt at the ends, and brushed-cobalt loops (swags) and tassels along the shoulder. On the reverse are two simple tassels of four paired leaves. The rim resembles wares produced in Rockbridge County; the handles, however, resemble some Morgan-Wilson-related vessels from Staunton, Virginia.
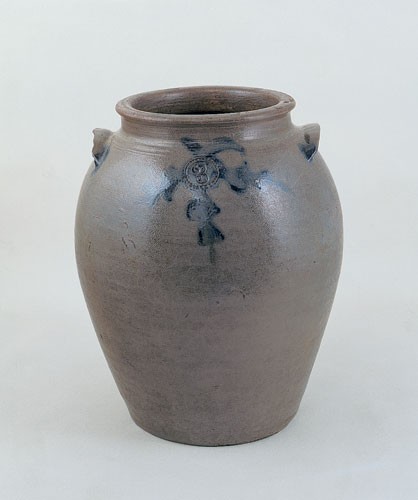

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) This recently discovered vessel has the attributes of form and decoration that define Group 3. The important incised inscription on its base—“Richmond”—defines the area of manufacture.

Detail of the inscription on the base of the jar illustrated in fig. 43.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 11 1/4". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Kurt C. Russ.) The bold, incised ridges at its shoulder, the slightly curved earlike handles with blue only at the terminals, and the impressed capacity stamp (“2”) encircled with teeth and incorporated into a blossom that extends upward from four opposing single-stroke brushed leaves resemble decorations on vessels illustrated in figs. 42 and 43.
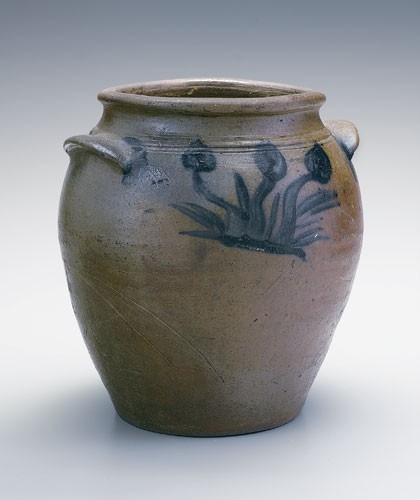

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 9". Capacity: approx. 1 gallon. (Private collection; photo, Kurt C. Russ.) On the concave of the reverse side of this storage jar are two or three deeply incised concentric lines intersecting with slightly curved, flaring earlike handles with blue at each end.

Pitcher, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/4". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) The capacity stamp of this oversize pitcher is incorporated into a blossom with blue horizontal lines at the spout. The decoration as well as the stamp style are very similar to those on the storage jar illustrated in fig. 58.
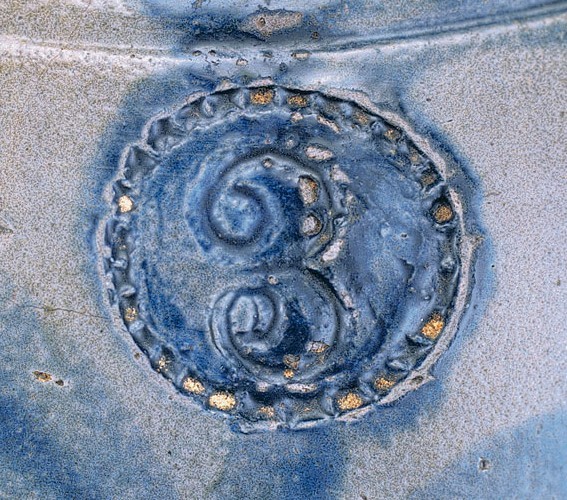

Detail of the capacity stamp on the pitcher illustrated in fig. 47.

Pitcher, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.)
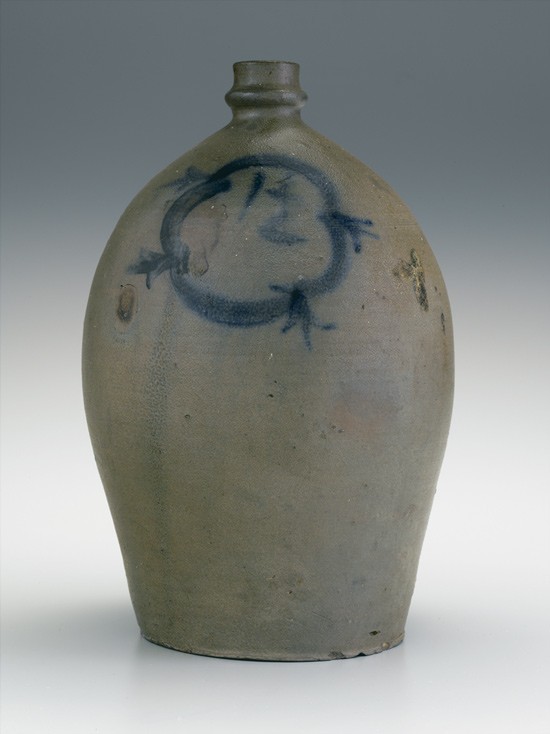

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12 1/4". Capacity: 1 1/2 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Kurt C. Russ.) The decoration on this jug features a simple brushed-cobalt circular wreath accented with four outwardly projecting tassels. Within the wreath is a brushed capacity mark (“1 1/2).

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 9 1/2". Capacity: approx. 1/2 gallon. (Private collection.) This jug was attributed to Rockbridge County in H. E. Comstock, Pottery of the Shenandoah Valley Region (Winston-Salem, N.C.: Museum of Early Southern Decorative Arts, 1994), p. 457, fig. 7.7. Its form is virtually identical to the jug illustrated in fig. 50, whereas its decoration is similar to that on the jar illustrated in fig. 64.
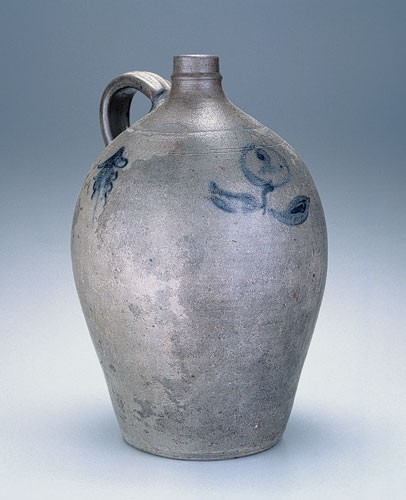

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.) The tassels decorating this jug are similar to those on the reverse of the jar illustrated in fig. 43.

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817-1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/4". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Kurt C. Russ.) The cobalt wreath motif encloses the capacity mark (“2”) of this ovoid jug.

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Carole Wahler.) This ovoid jug is decorated with a primitive brushed-cobalt rabbit with upright ears.

Jug, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection; photo, Ralph Arthur.) Mirroring the form of the jug illustrated in fig. 54, this piece features a primitive brushed-cobalt owl; it is also pictured in Kurt C. Russ, “Exploring Western Virginia Potteries,” Journal of Early Southern Decorative Arts 21, no. 2 (1996): 115, fig. 10.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12 1/2". Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.) The floral decoration relates to that on the jar illustrated in fig. 43. The stamped capacity mark (“2”) is identical to that illustrated in fig. 45 but without the encircling teeth.

Detail of the capacity stamp of the jar illustrated in fig. 56.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) The form of this stoneware jar is typical of Schermerhorn—thick walls and a rounded rim, like those within the first group, embellished with the rather customary floral device (leafy vine with bloom)—yet on its reverse the brushed-cobalt wreathlike motif with tassels enclosing the capacity mark (“3”) is a decoration that specifically relates to the third group.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12 1/2". Mark: stamped “2” in dotted circle placed in center of brushed blue cobalt floral bloom. Capacity: 2 gallons. (Private collection.) The rolled applied handles of this jar are identical to those on the jar illustrated in fig. 56. The capacity mark is identical to those on the vessels illustrated in figs. 43, 45, and 47, suggesting that they are all from the same pottery.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 16 1/4". Mark: incised “4.” Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.) This stoneware jar is very similar in form and decoration to the jar illustrated in fig. 59; its handles, however, are flattened, slightly curved with blunt ends, as those on the jar illustrated in fig. 45.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 12". (Private collection.) The simple brushed-cobalt flower decoration—two opposing leaves supporting a stem with a circular open bloom—is similar to that on the jug illustrated in fig. 52.
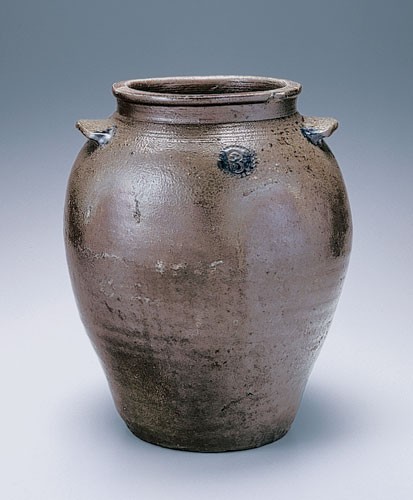

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14". Mark: stamped “3” within a circular toothlike border. Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) Found in central Virginia, this ovoid stoneware jar has an elongated neck (1"+) resembling DuVal wares, a flat rim, three concentric incised lines at the collar, and slightly curved earlike handles with blunt ends resembling those from both Richmond and Rockbridge County.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 15 1/2". Capacity: approx. 4 gallons. (Private collection.) This vessel has a diminutive squared-off rim above a pronounced 3/4-inch collar similar to that illustrated in fig. 64. The cobalt swag-and-tassel decoration on the front resembles the decoration on the jar illustrated in fig. 42. On the reverse is a single floral motif with a “lollipop” bloom.
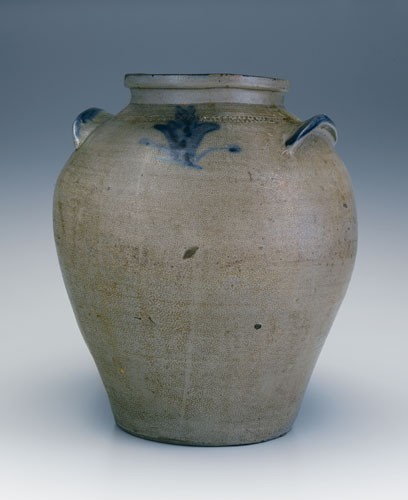

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 14 1/2". Capacity: 4 gallons. (Private collection.) The jar illustrated here has a diminutive squared-off rim above a pronounced 3/4-inch straight collar, impressed coggle wheel impressions at the shoulder, and slightly curved, flattened earlike handles with blunt ends accented with blue cobalt. The front is decorated with a simple multi-leaf floral motif, and on the reverse is a tassel.

Detail of the handle and the impressed decoration of the jar illustrated in fig. 64.

Storage jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Samuel Wilson, and/or associates, Richmond or Henrico County, Virginia, 1817–1850. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 13 3/4". Capacity: 3 gallons. (Private collection.) This vessel form is very similar to the piece illustrated in fig. 62.

Jar, attributed to John P. Schermerhorn, Richmond, Virginia, 1811–1837. Salt-glazed stoneware. H. 11 3/4". Mark on base: stamped “.J.P:S:” (Private collection.)
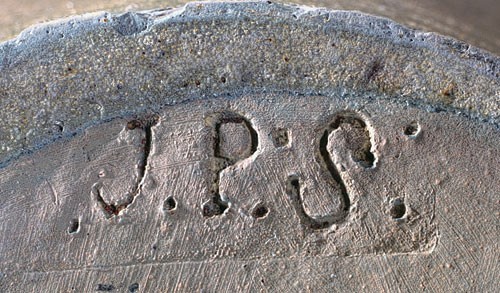
Detail of the initials stamped on the base of the jar illustrated in fig. 67.

Photocopy of John P. Schermerhorn’s signature, taken from the 1820 Census of Manufacturers, Henrico County, Virginia.
John P. Schermerhorn[1] was born on July 22, 1788, in Schodack Township, Albany County, New York. He is first identified as a potter in 1814, working in Benjamin DuVal’s stoneware manufactory in Richmond, Virginia.[2] The documentation and evaluation of Schermerhorn’s production at DuVal’s, and subsequently at his own Richmond factory at Rocketts, provide a fascinating story illustrating a wide range of stoneware forms and decorative techniques previously undocumented for eastern Virginia. The wares also strongly reflect Schermerhorn’s training in the early Germanic/Dutch stoneware tradition, which had been transplanted to New York–New Jersey. Despite his forty-year involvement in pottery manufacturing in Virginia, only now are we beginning to understand his production and appreciate the influence he had on the nineteenth-century stoneware industry in eastern Virginia.
In an effort to understand more fully the nature of John P. Schermerhorn’s involvement in the early Richmond stoneware industry, a multifaceted research approach was undertaken that included four major components: (1) a consideration of his place of origin, historical and genealogical background, previous involvement in the pottery industry, and those for whom he apprenticed, was trained or employed by, or otherwise influenced; (2) a thorough assessment of his activities in Richmond, and in Henrico and Charles City counties, including the identification of potteries there with which he was associated, as well as those individuals he worked for, worked with, or those he employed; (3) documentation and analysis of extant wares signed by or attributed to him, with emphasis on vessel attributes including form (rim configuration and handle style), maker’s or capacity marks, and decoration (brushed or slipped blue cobalt, incising, decorative stamps, or coggling); and (4) an examination of archaeological materials collected or excavated from regional pottery manufacturing sites and comparison of these with surviving regional extant wares.
Historical and Genealogical Background
Exploration of Schermerhorn’s family history and genealogical background is relevant to understanding his role in early Virginia stoneware production in Richmond and his influence on Virginia pottery traditions southward along the James River and in central Virginia. Having descended from the Schermerhorn family of New Amsterdam–New Netherland whose immigrant patriarch from Holland was Jacob Janse Schermerhorn (1622–1688), John P. Schermerhorn, born an even century after his ancestor’s death, was destined to be an important figure in the history of ceramics in Virginia.
The limited documentation of John P. Schermerhorn’s specific family branch notwithstanding, we now know that the John Peter Schermerhorn identified as an early Richmond potter by Rauschenberg in his seminal work on DuVal’s early Richmond pottery[3] was actually one John Poole Schermerhorn. This is clear given that no other John P. Schermerhorn living and working in Richmond during this time can be identified other than the one whose will of record there references his middle name—John Poole Schermerhorn (1788–1850). Moreover, the inventory and appraisal of John Poole Schermerhorn’s estate includes one lot of stoneware worth two hundred dollars and lists fixtures in a factory valued at two dollars.[4]
The family motto, “Industria Semper Crescam” (By industry I will succeed), aptly characterized the family’s strong connection to shipping, industry, and commerce from the late seventeenth through the early nineteenth century (fig. 1). Jacob Janse’s son, Jacob Jacobse Schermerhorn (b. 1662), was master of the sloop Star, plying between Albany and New York from 1681 to 1684; his brother Cornelius was subsequently master of the same vessel, which apparently was owned and used by their father in connection with his earlier trading and exporting business. Little documentation of John P. Schermerhorn’s immediate ancestors’ involvement in maritime commerce has surfaced. However, John P. Schermerhorn clearly descended from one Jacob Janse Schermerhorn, who in 1636, at age fourteen, traveled to New Netherland on the ship Rensselaerswyck. The extended family’s association with business enterprises and shipping for the next two centuries is well documented in the New York region, with Peter Schermerhorn Sr. establishing, about 1811, a slip and countinghouse on the East River in Lower Manhattan (now known as Schermerhorn Row).[5]
Family genealogical records suggest that John Poole’s father may have been a Cornelius Schermerhorn born circa 1755–1765. Indeed, it is well known that Cornelius is a common given name among Schermerhorns, one that continues from 1828 to the present in the Henrico County family of descendants of John Poole Schermerhorn.
Schodack, in Albany County, New York (after 1790, Schodack Township, Rensselaer County), is identified as the family seat of this Cornelius Schermerhorn and, at least for a brief period, that of his son, John Poole. Genealogical records indicate that John Poole lived in New Jersey before 1810, when he moved to Virginia. However, understanding precisely who his father was, and knowing the elder’s whereabouts at any particular time, is problematic, although it is believed that he was born, and died, in Schodack.[6]
Exhaustive genealogical research into which Cornelius was John Poole’s father has narrowed the candidates from at least nine to three.[7] Some of them had associations with maritime commerce between northern ports (New York, Philadelphia, and Boston) and more southern ones (Norfolk, Virginia; Charleston, South Carolina; and Edenton, North Carolina, to name a few). We look to future research to pinpoint precise family associations. Clearly the Schermerhorns were engaged in extensive commerce along the eastern coast, distributing pottery they produced and used aboard their own ships as well as shipped to other ports.[8]
John Poole Schermerhorn may have begun his potting career in the Albany-Troy area of the Upper Hudson Valley. It was here that potter Branch Green operated/managed a rather poorly understood pottery—the Morgan (James Morgan Jr.) and Smith Stoneware Factory—which also employed potter Rowland Clark. Schermerhorn’s initial contact with Branch Green appears to have been between 1799 and 1802, in “the South-East part of the village [of Troy].” Advertisements in 1799, 1801, and 1802 sought shop boys and journeymen potters; in 1801 they sought apprentices to the potters trade.[9] It seems probable that young Schermerhorn responded to these advertisements and began a working relationship with Green, starting as a shop boy, then as an apprentice, somewhat later as a journeyman potter, eventually culminating between 1803 and 1805 in their arrival at Middlesex County, New Jersey, where they established themselves with the Morgan, Van Wickle, Green concern. (Schermerhorn’s apprenticeship likely bound him to Green and, as a consequence, later to Morgan.) This South Amboy vicinity broadly included the pottery regions of Old Bridge and Cheesequake.
The association of Schermerhorn with the Morgan, Van Wickle, Green Pottery of Old Bridge, New Jersey, is confirmed by a document dated May 27, 1809, whereby John Schermerhorn obtained a $300 mortgage loan from James Morgan Jr., pledging,
The one equal half part of all the lot of land situate in North Brunswick . . . lying on the north side of the main road leading from Spotswood to the old south river bridge [Old Bridge]. Beginning at a stone planted for a corner distant eighty two links [about 54 feet] on a course south- . . . and east . . . from the most southeasterly corner of the pot house. . . .[10]
This mortgage was witnessed by Sally Van Wickle and Margaret Sophia Van Wickle, both daughters of one of the factory owners. The land on which the pottery was located is described as containing 31/100ths of an acre (fig. 2).
Schermerhorn may have taken over Green’s interest in the concern after the latter departed to Philadelphia in 1809 to establish a stoneware pottery.[11] By this time Schermerhorn had completed his apprenticeship to Green or Morgan and, approaching the age of twenty-one, was now in a position to pursue his own independent business relationships, activities, and interests. Although no cancellation of Schermerhorn’s mortgage loan has been located, all available evidence suggests that Schermerhorn’s ownership interest in the Morgan, Van Wickle, Green pottery was of shorter duration than was Green’s, as Schermerhorn moved to Virginia after only a year or so.[12]
Being situated opportunistically between New York City and Philadelphia and only five miles from the county seat at New Brunswick, John Schermerhorn’s purchase in 1809 of the 1/2-acre lot in New Jersey occurred in the hotbed of ceramics in America—South Amboy, Middlesex County, the narrow midsection of the state indented by the Raritan Bay on the north and, on the northeast, by lower New York Bay, Staten Island, and Long Island. This twenty-five-square-mile area of salt marsh and pine barrens, with Roundabout (now Sayreville) and South Amboy at the upper corners, Old Bridge and Cheesequake at the lower corners, and the Morgan Clay Banks and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, contained the finest grades of clay known to preindustrialized America.[13] Stoneware potteries were established in each of these locations, and, as all were within five or six miles of each other, provided excellent networking opportunities for itinerant pottery workers within the area’s perimeter (fig. 3). Many of the older regional maps show families of potters living next to each other or otherwise in close proximity.
Old Bridge (or Old South River Bridge) is drained by the South River, which flows south–north toward the Raritan River and thence to Raritan Bay and the Atlantic. The headwaters of Cheesequake Creek had a succession of potters, starting with Captain James Morgan Sr. and his son and namesake, from whom John P. Schermerhorn obtained his mortgage and land with pot house. Although this area was the hub of the Morgan and Company pottery, it was by no means the Morgans’ only business interest. Eventually the pottery of Thomas Warne and Joshua Lett succeeded the Cheesequake location, and, in the first decade of the nineteenth century, Morgan, Van Wickle, and Green established the Old Bridge concern there.[14]
This backwater was sparsely settled, and clay mining and stoneware manufacture became quite important to sustaining the area. Ready supplies of Amboy stoneware clay and Woodbridge clays attracted many fine potters to the area on a consistent and sometimes rotating basis.[15] Even the great potters of the Remmey, Crolius, and Commeraw families are known to have spent a portion of their time and labors in this neighborhood. While close business and personal relationships were secured among the Morgan, Van Wickle, Warne, and Lett families through important intermarriages, succession by estate of adjacent lands with potteries was also facilitated.[16]
Despite the valuable pottery-related experience Schermerhorn had gained through his association with Morgan, Van Wickle, and others, he probably realized early on, as did Green, that the presence of the tight-knit Old Bridge families made unlikely his ability to establish, expand, or advance his own concern, or be the beneficiary of a pottery by succession. His decision to move to Virginia was probably influenced by two additional factors. First, he might have seen opportunity when the United States was denied access to English wares through the Embargo Act and Non-Intercourse Acts, making it necessary for ceramics to be increasingly “homegrown.” Second, being part of a shipping family, he might have thought it would serve him better to escape the New York blockade and pursue markets for stoneware in coastal cities to the south of his home state, which was heavily pressed as a result of trade restrictions. The pursuit of these markets perhaps revealed not only sites for successful commerce, but pottery-related employment opportunities and potential locales for establishing stoneware manufacturing centers.
Schermerhorn in Richmond and Henrico and Charles City Counties
Genealogical research suggests Schermerhorn went to Virginia by 1810.[17] Assuming his enlistment in the 19th Regiment Virginia Militia occurred at the inception of the War of 1812, Schermerhorn can be placed in Richmond by March 1813,[18] although there is some speculation that he arrived in Charles City County, Virginia, before coming to the Richmond area.
Benjamin DuVal’s 1791 advertisement for potters set the stage for the arrival of Schermerhorn and other stoneware potters, although it was not until 1811 that DuVal expanded his business as an outlet for stoneware by opening the Richmond Stoneware Manufactory, formerly Benjamin DuVal and Co. Other individuals previously associated with the manufacture of pottery in New York, and who moved to the Richmond area of Henrico County in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, were likely associated with DuVal’s operation(s). In addition to Schermerhorn, we know of William Harwood (1811–1815), who had previously cooperated with DuVal in the formation of the Richmond Tile Manufactory (a roof tile business) in 1808, and Samuel Wilson (circa 1817).[19]
By 1813 Schermerhorn was living close to (if not in) Richmond and working at Port Mayo, between Rocketts Street, Nicholson Street, and Gillie’s Creek. This location likely included a residence, a warehouse, as well as, perhaps, a kiln. Young’s 1809 map of Richmond shows the contiguity of this lot to the actual slips of the Port Mayo shoreline at Rocketts (fig. 4). The Richmond City tax records of 1815 list a Sarah Lester as owning Port Mayo property with warehouses, and John Lester’s wharves are clearly marked on Young’s map. John Poole Schermerhorn does not show up on this list, although records show that in 1818 he was paid for gunpowder storage at a Richmond warehouse facility during the 1812–17 period.[20] This suggests a possible lease or rent agreement between Schermerhorn and the Lesters.
During the same period Schermerhorn joined the 19th Regiment Virginia Militia, 2nd Brigade, 4th Division, as a private under Colonel John Ambler’s command.[21] Within the 19th Regiment, which was composed mostly of Richmonders, Schermerhorn served in Captain Robert Gamble’s Troop of Cavalry, as well as in Captain Anthony Turner’s Company in the service of the United States during the War of 1812. He was credited with one-and-a-half month’s service (fewer than three months was the norm, even for commanding officers). A few units of Richmond’s militia were sent to Norfolk in March 1813, and a few turned out in March and June 1813, when the British appeared to threaten the capital. In the summer of 1814 other units were called to duty and encamped near the city with the brigades of Generals Porterfield and Chamberlayne. John Poole is listed in the archived Virginia Militia muster rolls for this unit, and it is likely that it was in this capacity he was approached by Richmond city officials about storing gunpowder shortly after the 1812 conflagration.[22]
DuVal’s informative 1814 advertisements, cited previously, are significant because they not only identify Schermerhorn as a potter but indicate that he is “concerned in one of my shops.”[23] Schermerhorn’s response to DuVal’s ad, published in the Daily Compiler, expressed his discontent with its characterization of his limited involvement (fig. 5).[24]This bold adversarial response is probably reflective of Schermerhorn’s frustration with DuVal’s management, a growing confidence and self-assurance of his skills and contribution to DuVal’s production, and a desire for independence and appropriate recognition for his growing role in this early Richmond industry.
Another reference, perhaps suggestive of Schermerhorn’s increasing importance as a manufacturer, is one that appeared in an advertisement in the Virginia Argus, which mentions his appointment to a committee to draft a constitution for the Mechanical Society, which had met at the Washington Tavern on June 6, 1814.[25]
Richmond Factory at Rocketts
In 1817 Schermerhorn married Sarah Christian Wilson (probably of Charles City County) at St. John’s Church on Richmond Hill (later Church Hill). He also apparently left his employment/association with DuVal’s concern and established his own stoneware pottery in the city. On December 6, 1817, “Jno. P. Schermerhorn” is listed as occupying two brick buildings or dwelling houses with slate roofs—insured for three thousand dollars each—in Rocketts, located south of John Lester’s lot and bordered by Nicholson Street on the southeast and Gillies Creek on the northwest (see fig. 4).[26] This was an excellent location for Schermerhorn’s enterprise, being located near the south end of Rocketts Street adjacent to Rocketts Warehouse and Landing and in close proximity (a few blocks) to a major wharf along the James River, thereby facilitating receipt of supplies and shipment of wares. Apparently Schermerhorn prospered while leasing property in this immediate vicinity from the Lesters and made the decision to invest further and expand his concern there. It is possible that this is the same property previously utilized by the DuVal family in their business activities before divestment in 1816–17.
Confirming Schermerhorn’s continuing operation is the 1820 Manufacturers Census for Henrico County, which lists one “John P. Schermerhorn, Potter,” who makes use of “50 Tons of Clay, 80 Cords Wood, 18 Sacks Salt, &c. at value of $350, employing 3 men, no boys, 1 kiln and 3 wheels, with $300 wages and $500 other expenses, to produce ‘Stone Ware of all Kinds.’”[27]
Identifying the three employees is problematic; several lines of documentary evidence suggest, however, that Schermerhorn had alliances and close associations with other potters also identified in the 1820 census records. In some cases these associations appear to have originated in New York, continued in Richmond with DuVal’s operations and then into Schermerhorn’s own pottery there, and, ultimately, resulted in the establishment of potteries south along the James River in Henrico County and—possibly—in Charles City County. These other potters include, in addition to Samuel Wilson and William Harwood mentioned previously, Samuel Frayser and Thomas Amos, both of whom appear in the 1820 Henrico manufacturers census.[28] It is likely that between 1817 and 1820 most if not all of these individuals worked with, for, or as competitors with Schermerhorn.
Further information is provided by an 1820 advertisement placed by Schermerhorn in the Richmond Commercial Compiler announcing a large and general assortment of stoneware, with reference given to his “Port Mayo, near Rocketts” location. Specific sites where wares could be seen and orders placed are listed, and there is an offer of free delivery in four hours within the city (fig. 6).[29] Transportation of Schermerhorn’s wares within the city was by dray or cart, and, when not provided gratis as offered in this advertisement, may have included costs similar to those listed in an advertisement in the 1819 Richmond city directory.[30] Other obvious forms of transport of finished products included bateaux along James River distribution points and, of course, sloops, schooners, and other shipping able to navigate to Port Mayo, Richmond, below the falls of the James. In the first decade of the nineteenth century, as a result of the completion of two canals, rock clearing, and wing dams that channeled the water in shallow stretches, the James River was navigable by bateaux to the Lynchburg area, and by 1816 passage was possible through Balcony Falls to Buchanan. By 1840 the James River and Kanawha Company completed the canal “at a safe remove from most of the river and now accommodating the mule-pulled packet boat” to Lynchburg, and by 1851 some 197 miles of canal were completed to Buchanan; transportation was possible to Lexington shortly thereafter.[31]As westward expansion through the Cumberland Gap and wagon roads south accelerated, such an outlet became both crucial and expedient.
In 1820 the value of the buildings on the 1/2-acre lot occupied by Schermerhorn was assessed at the substantial sum of $2,000. By 1821, however, those improvements had dwindled to $1,200, suggesting a decline in his business operations and/or activities or maintenance of same. He was able to thrive even during difficult financial panics and contractions in the market largely due to the utility and quality of the wares he produced. In fact, in 1825 he acquired sixty-eight acres located only two miles north of the county courthouse. Meanwhile, the value of the improvements on his Port Mayo lot increased to $5,000.[32]
Family Life and Montezuma
John Poole did have a productive family life. His first wife, Sarah Christian Wilson, bore him two children—Mary Christian and William Francis (“Frank”). She died in 1822 at the age of twenty-four, likely during or shortly after childbirth. His second marriage, to Mary Shields Parkinson on May 3, 1827, led to five more children—John Poole II, Isabella Irving, Egmont Parkinson, James Cornelius, and Richard Everett, who died in infancy. The family lived at Montezuma Farm, southeast of Mechanicsville Turnpike (now US 360) in the Fairfield Township section of Henrico County, approximately one mile northeast of Richmond. Construction of this home on a tract of land, apparently consisting of some 89–102 acres by this time, occurred between 1827 and 1830 (figs. 7, 8). Montezuma is prominently depicted on several major maps constructed during the Civil War as located in the vicinity of the tollgates east–southeast of the road, on an imposing knoll overlooking the pike. It seems that property on both sides of Mechanicsville Pike was owned by Schermerhorns, as the “Est. of Schermerhorn” is clearly marked on the aforementioned maps as well as on a recorded plat and deed indicating the property is northwest of the pike. These maps show familial relationships of extended in-laws and even those having business relationships with John Poole Schermerhorn Sr. (DuVal property within five miles of this area—along the Chickahominy River in the area of Henrico County’s Fairfield District, toward Mechanicsville and New Bridge—was also advertised for sale. The land adjoined or was near land owned by Christians, Fraysers, Harwoods, Smiths, and other DuVals.)
Adding to his Henrico County holdings, in 1830 John P. Schermerhorn purchased a tract of land from the estate of one Francis Wilson in Charles City County, Francis having died “seized and possessed.” The sale took place on the courthouse steps, with John P. Wilson (presumably his son) acting as his representative.[33] It is possible that this John Wilson was Schermerhorn’s brother-in-law (i.e., his first wife’s brother). Equally plausible is the idea that the land in question included Wilson’s Landing, often referred to as a site of pottery manufacturing. This tract was also referenced as including Sandy Point and Teddington (where, in 1869, a granddaughter was born).
Although unconfirmed, it is likely that Schermerhorn purchased this land, which included an ongoing pottery (or previous operation), and became affiliated with it after leaving his Richmond concern about 1837 or later. Tax credits show him as owner of two lots on Church Hill and one on K Street in Richmond, each having improvements. In 1847 he acquired 167 acres called Whitlows that was located about seven miles southeast of the Henrico County courthouse.[34] It appears he maintained his residence at Montezuma, for when he died on February 19, 1850, he was buried in a family cemetery there. It is not known whether the factory mentioned in his will—fixtures from which are valued at two dollars—refers to a kiln on his land here or elsewhere in Henrico County, a pottery on the Charles City County tract, or a working kiln retained at Rocketts. His total personal property, not including cash and real estate, was valued at $2,548 in his inventory and appraisal in 1850.[35]
Schermerhorn Stoneware
With limited documentation of the potters working at the DuVal pottery factory, the assumption is that Schermerhorn, William Harwood, and/or Samuel Wilson were responsible for the production of those extant wares and waster sherds stamped “B. DuVal, Richmond Va.” That the vessel forms, maker’s mark, and decorative treatments represented in the recovered assemblage relates to early New York–New Jersey manufactured stoneware is without question.
The discovery of a few signed examples of wares produced by Schermerhorn at his own Richmond stoneware manufactory allows a definitive attribution to his pottery of other surviving wares with related form, decorative treatment, handle, capacity designation, color, rim configurations, and so forth. Initial examination of available wares by Schermerhorn resulted in the identification of two basic groups based on vessel form and, to some extent, intragroup similarities in decoration.
Group 1 is defined by some extant vessels (figs. 9, 10) bearing his stamped factory mark (fig. 11). All exhibit thick-walled, evenly glazed ovoid forms with prominent rolled or well-defined rims and highly placed rolled or extruded applied handles covered with blue cobalt (at their intersection with vessel body). These forms also display brushed blue cobalt floral motifs depicting leaves or vines with interspersed opposing blossoms or peach-shaped blooms, usually on both vessel sides, with brushed blue numeric capacity designations frequently placed under the handles (see fig. 10, right).
Schermerhorn’s maker’s mark—“RICHMOND FACTORY, Virga, J. P. SCHERMERHORN”—appears to be unique to Virginia ceramics (see fig. 11). The curved, stamped, bannerlike configuration and overall size, the Richmond Factory designation including place-name, the abbreviation for Virginia with the superscript a, and the centrality and symmetry of the large g are striking, especially with regard to the inclusion of stamped flourishes or fleur-de-lis flanking it on both sides, and the capitalized typeset lettering and blue highlighting.[36]
Several related, unsigned ovoid storage jars identified during the course of this research range in size from one to five gallons, with variations noted (probably relating to available surface area) in brushed decorative treatments. Two loosely defined categories of decorative treatments exist within this first group. The first are incised decorative treatments clearly related to early New York–New Jersey stoneware. Recorded examples include a bold federal-style eagle with blue cobalt (fig. 12), a clipper ship (fig. 13), a fish or serpent, a standing bird with cobalt flower and festoons (fig. 14), a crowing rooster (fig. 15), a soldier in military helmet, and an incised heart with arrow.
The second decorative treatment is brushed or slipped cobalt decoration. This category has four basic subsets: alternating multipetaled leaves (figs. 16, 17); undulating vines with leaves and opposing rounded blooms or similarly composed floral spray, the size and number of blooms relating to the surface area available (figs. 18-23); double or single horizontal leafy vine with terminating floral bloom(s) surrounded by open petals (figs. 24- 27); and human or animal motifs (figs. 28, 29).
The floral spray with opposing blossoms is by far the most common decorative motif used by Schermerhorn to embellish his wares. The frequently encountered and consistent cobalt decoration combines elements of both the physical and the metaphysical, from the abstract basic “watch-spring” or concentric circular patterns learned during his apprenticeship at South Amboy to his more realistic patterns, which replace the springs or circles with fruits or blossoms and the leading central “swoosh” with flowing or undulating vines. This “swoosh” also could be interpreted on the scale of the metaphysical from a mathematical standpoint, as it represents portions of symbols of both approximation and infinity.[37]
Group 2 of Schermerhorn wares relates to a recently discovered vessel (fig. 30) with the profile of a man—perhaps a self-portrait—and the lettering “JOHN P.,” both incised, to the left of and across the figure’s midsection (collar), with brushed blue applied to the hairline, facial features, and neck (fig. 31). The now familiar blue script capacity mark appears on the reverse side of the vessel rather than under each handle as in Group 1. Frequently seen on both sides of related examples devoid of incised decoration is a blue capacity designation, often underscored with two or three horizontal lines of decreasing length, with a terminating squiggle or initial that some have interpreted as representing either a J or an S and, hence, the maker’s signature. This group of wares is generally characterized by thinner-walled, more elongated ovoid forms with evidence of the potter’s turning marks often visible on the vessel’s exterior, somewhat smaller handles usually devoid of blue decoration, and a medium- to dark-gray clay. Recorded vessel capacities include one, one-and-one-half, two, three, four, and five gallons (fig. 32). Another significant example within this group is a three-gallon vessel with the brushed blue cobalt date “1837” along its side and characteristic brushed capacity mark “3” on the reverse (fig. 33). It is likely that the date commemorates a national and/or regional political event, or perhaps a significant date for his pottery business.
Connecting Groups 1 and 2 are two recently discovered, beautifully potted two-gallon ovoid jars, each with a pronounced neck and highly placed applied crescent handles exhibiting a horizontal floral decoration of undulating vines and blossoms on its face, with the reverse showing a centrally placed “2” underscored with three horizontal lines of decreasing length and a J-shaped squiggle or initial below (fig. 34).
Before the discovery of these two pieces and the incised self-portrait crock (see fig. 30) the relationship between these two groups was unknown. We can now state with confidence that all were produced at Schermerhorn’s pottery and illustrate variation within an assemblage of surviving wares from the same pottery perhaps reflective of temporal variation in the forms produced or of the work of different decorators or potters within the same firm.
In addition to the ubiquitous ovoid storage-jar form that dominates the assemblage of surviving Schermerhorn wares, several other vessel forms are recognized: jugs (figs. 35, 36), pitchers (figs. 37, 38), and flasks (figs. 39-41). Schermerhorn’s 1820 advertisement indicates production of “stoneware of all kinds,” suggesting a range of forms mirroring those listed in DuVal’s newspaper advertisement.[38]
The distinctive Schermerhorn wares have remarkable similarities with later wares produced at several potteries located south of Richmond along the James River as well as some identified from central Virginia by related, unidentified potters. Schermerhorn may have had direct involvement with some of these potteries or those trained or influenced by him may have been responsible for their establishment.[39]
Another group of extant wares from the region are thought to be made either by Schermerhorn himself or with an associated potter at Rocketts, most likely Samuel Wilson. This third group (Group 3) is characterized by well-potted, wonderfully ovoid vessels with varying rim configurations, frequently the presence of one to three concentric incised lines at the vessel’s shoulder, and rather simplistic brushed blue cobalt decoration involving swags and tassels, simple petaled or bilateral leaved flowers, or large primitively composed animals, sometimes associated with a distinctive capacity stamp usually encircled by a toothed border or outline. This unusual capacity mark is often incorporated into the floral decoration as a blossom or flower. Representative forms include storage jars (figs. 42-46), including one ovoid jar with “Richmond” incised on its base, pitchers (figs. 47-49), and jugs (figs. 50-55).
The decorative treatments within this group are more minimal and less detailed than the flowing vines and flowers on Schermerhorn wares in Group 1, which appear to have been executed by the hands of an artist. Pieces have been collected in Richmond, as well as in Augusta, Botetourt, Buckingham, Dinwiddie, Montgomery, Rockbridge, and Rockingham counties.
The ovoid storage jar with the incised “Richmond” (figs. 43, 44) enables us to identify the origin of these vessels, and several of the jugs—albeit with decoration that suggests another decorator or associated potter—have forms identical to those by Schermerhorn. Bolstering our attribution of these wares to the Schermerhorn factory is a “transitional” vessel exhibiting standard Schermerhorn florals (Group 1) on the front (see fig.34, right) and, on the reverse, decoration consisting of four leafy branches radiating from a circular rounded floral element with “2” stamped in its center, which characterizes Group 3 (figs. 56, 57). Another vessel that illustrates the relationship of this group to those of Group 1 is a three-gallon ovoid salt-glazed stoneware storage jar of standard Schermerhorn form with thick walls and a rounded rim (Group 1) embellished with the rather standard floral device (leafy vine with bloom) and yet, on the reverse, the brushed-cobalt wreathlike motif with tassels encloses the capacity mark “3” (fig. 58)—a decoration specifically relating to this third group—that also appears on the jug illustrated in figure 50.
Included within the latter grouping of wares from Rocketts are some vessels of slightly different form, sometimes lighter clay, often identical decoration (swags, tassels) sometimes in combination with a distinctive simple flower with a round blossom or “lollipop” flower, and closely related handles and capacity marks (figs. 59-61). Three very similar vessels have a distinctive squared-off rim above a well-defined, straight-sided collar or neck, one exhibiting the characteristic capacity mark (fig. 62), another combining the lollipop flower with swag-and-tassel decoration (fig. 63) very similar to that on the front of the jar illustrated in figure 42, and a final example impressed with a band of impressed coggle-wheel decoration at its shoulder (figs. 64, 65). Although deeply incised tightly grouped lines or shallow incised concentric lines have been observed on many vessels from this group, this is the only known example to exhibit the coggled decoration, which appears to be strongly related to Morgan wares from Old Bridge, New Jersey. Interestingly, the cobalt decoration on this large jar is almost identical to that on the small ovoid jug shown in figure 51. The swag-and-tassel brushed-cobalt decoration seen on the vessels in figures 42,56, and 63 very closely resembles that seen on several pieces made by Commeraw at Corlears Hook, as well as on a couple of pieces stamped “Made in South Amboy” that no doubt were produced during his brief period of activity in that area.[40]
Also recently discovered is a series of ovoid stoneware storage jars with flat protruding rims, straight collars ranging from 1 to 1 1/2 inches in height, turned flattened blunt-ended handles, and free-flowing brushed blue cobalt swag-and-tassel motifs on their upper shoulders (fig. 66). It is suspected that these pieces were made at Rocketts by Samuel Wilson working in conjunction with Schermerhorn and thus fit within this third group, being reminiscent of the Commeraw and Morgan wares.
Another recent discovery attributed to Schermerhorn is a 1 1/2- to 2-gallon ovoid jar with a well-formed, flattened rim and two bands of incised concentric lines highlighted with blue cobalt, strongly reminiscent of the Morgan wares from New Jersey, and stamped on the base “.J.P:S:” (figs. 67, 68). This vessel lends support to the suggestion that Schermerhorn either trained or apprenticed in New Jersey.[41] A three-gallon pitcher with a capacity mark identical to that observed in figures 48 and 57 exhibits brushed blue cobalt decoration strikingly similar to examples made by the Morgans in New Jersey (see fig. 49).
While the extant forms stamped “B. DuVal” show well-potted forms and strong Germanic/Dutch influences (bulbous ovoid shapes, horizontal open-loop handles, incised jug necks, elongated vessel necks or collars, earlike flaring handles with blunt rounded edges, and smooth exteriors with even glaze), it is suspected that these wares represent the earliest production at the DuVal pottery, perhaps involving other undocumented potters who migrated from New York and worked in conjunction with Schermerhorn and Wilson. The later forms produced by Schermerhorn at Rocketts and those showing his influence along the James River to the south of Richmond are unquestionably distinct from the wares produced at the DuVal factory, as confirmed by extant signed DuVal wares and the analysis of wasters recovered from his kiln.
Summary
The now accurately identified Richmond potter John Poole Schermerhorn was a prolific and skilled artisan (fig. 69). Trained in a transplanted Germanic/Dutch stoneware tradition by early New York–New Jersey craftsmen, he successfully produced, marketed, and distributed his wares throughout eastern and central Virginia. As a result of business, family, and personal associations, Schermerhorn’s contribution to the history of ceramics in Virginia is a significant one. His association with Benjamin DuVal was fortuitous, as it provided an opportunity to test the Richmond-area market and participate in its ability to support and sustain an evolving pottery manufacturing concern involving not only Schermerhorn but, in all likelihood, many of his contemporaries and associates whose roles in this burgeoning industry are yet to be told.[42]
Schermerhorn apparently enjoyed a particularly close association with many members of the local pottery community. Understanding these associations is helpful in characterizing the broader nature of the potters and potteries of the Richmond area.
His coincident arrival in Virginia with that of Samuel Wilson, for example, suggests a prior association in New York, since both had resided in the Albany area. This might reflect the close, enduring relationships between potters that often were established at a relatively young age, either as peers (coworkers) or as subordinates to mentors (apprentice, journeyman, master potter). Both Schermerhorn’s and Wilson’s training in the northern Germanic/Dutch-influenced stoneware tradition is strongly reflected in their early-nineteenth-century stoneware production in Richmond and, in fact, helped define and ultimately shape the nature of eastern Virginia stoneware.
Schermerhorn’s working relationship with William Harwood and Samuel Wilson at DuVal’s concern, and likely later affiliation with Wilson at Rocketts, points to cooperation among potters and participation in different business endeavors.
His marriage to Sarah Christian Wilson, who was related to Samuel Wilson, illustrates the interconnectedness of pottery families. Moreover, the naming of their son William Francis Schermerhorn points to a possible tribute to both William Harwood and Francis Wilson.
Schermerhorn’s ownership of land adjacent both to Samuel Frayser and Harwood speaks to this closeness among potters (and their families) in that they frequently owned contiguous tracts of land. In many cases, clustering of potteries related to the proximity of natural resources (clay deposits) and population centers as well as shipping and distribution concerns, but in many specific cases in Henrico County the contiguous tracts related to residential and/or farming activity rather than pottery manufacturing.
Moreover, his purchase of land from Francis Wilson shows an expansion of his holdings and business endeavors. The transfer of land or potteries from one potter (or potter relation) to another—such as that from Wilson to Schermerhorn—was common in this area.
The importance of the potting industry to the area and the seriousness and high level of professionalism that these skilled craftsmen (and apparently quite savvy businessmen) brought to their work are suggested by Schermerhorn’s membership in the Mechanical Society.
Thus Schermerhorn’s story of potting in Virginia is replete with specific examples that illustrate the complex and fascinating associations between potters. This unique association combined with a strong work ethic characterizes the nature of their industry and provides the structure in which their operations blossomed and thrived.
The success of Schermerhorn’s endeavors can be measured in no small way by the remarkable assemblage of surviving signed and attributed wares produced (in the Richmond area) at DuVal’s Stoneware Manufactory, at his own factory at Rocketts, and perhaps at an unidentified kiln owned or strongly influenced by him. The documentation of these wares allows recognition that eastern Virginia stoneware potters embellished a full range of artistically produced forms with varying decorative treatments including incised and cobalt-brushed and -slipped blue floral, animal, and figural motifs rivaling those from other areas. Schermerhorn’s robust ovoid stoneware jars with flowing cobalt decoration exhibit a level of artistic talent seemingly in contrast with the thick-walled crock forms and primitively executed incised decorations involving ships, human profiles, eagles, hearts, and fish—all of which represent facets of his life experience.
The unique stoneware manufactured by Schermerhorn directly reflects his training and work with the Morgan Pottery at Old Bridge as well as his earlier experience in the Albany area of New York, which underscores the influence of the New York–New Jersey stoneware industry on the developing early-nineteenth-century stoneware tradition in eastern Virginia.
Rocketts’ red glare signaled to early-nineteenth-century Richmonders another firing of the local pottery kiln, which would yield a variety of utilitarian stoneware containers essential for their everyday household needs. More generally, it signified the role of Virginia artisans-citizens and commercial centers in the emerging republic and the budding industrialization of Richmond beginning in the federal period and extending into the second half of the nineteenth century. Today Rocketts’ red glare also symbolizes the enthusiastic response of ceramic historians to the identification and aesthetic appeal of these wares. It also celebrates their place in our greater appreciation and understanding of the history of ceramics in Virginia.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We extend a debt of gratitude to several individuals who provided significant contributions to this article: Brad Rauschenberg’s groundbreaking research on Richmond-area pottery provided a critical backdrop for our work; Robert Hunter participated behind the scenes, offering hands-on assistance and thoughtful comments; and Mary Gladue skillfully edited our cumbersome first draft.
W. Sterling Schermerhorn, a native Virginian, is a second great-grandson of the potter John P. Schermerhorn.
It has been suggested that John P. Schermerhorn was living in Charles City County in 1810 before making the move to Richmond.
Bradford L. Rauschenberg, “‘B. DuVal & Co/Richmond’: A Newly Discovered Pottery,” Journal of the Museum of Early Southern Decorative Arts 4 (May 1978): 56.
John Poole Schermerhorn’s will is recorded in Henrico County Will Book 13, reel 60, May 3, 1848, pp. 248–50, Library of Virginia, Richmond. For the appraisal of his inventory, see ibid., March 15, 1850, p. 378.
Richard Schermerhorn Jr., Schermerhorn Genealogy and Family Chronicles (New York: Tobias A. Wright, 1914). This is the most comprehensive Schermerhorn family genealogy to date, although it does, unfortunately, largely omit the John P. branch and Lucas J. lines. More information about the Schermerhorn family is available at www.schenectadyhistory.org/ families/schermerhorn/chronicles/index.html; and Early South Carolina Newspaper Database Reports, www.escndatabase.com. For information on the Schermerhorns of Virginia, see http://worldconnect.rootsweb.com/cgi-bin/igm.cgi?op=SHOW&db=psidiver&recno=1926.
Personal communication from W. Sterling Schermerhorn to Kurt C. Russ, October 6, 2003.
Barbra Kay Armstrong, comp., Index to the 1800 Census of New York (1984; repr. Baltimore, Md.: Clearfield Co., 1996), p. 30.
Twenty-first-century collectors have documented Schermerhorn wares turning up with some frequency in both North Carolina and South Carolina, reflecting the nineteenth-century shipment of these Virginia wares southward. This is not at all unusual, as Rauschenberg and others have noted the frequency with which New York (Crolius), Philadelphia, and Baltimore wares are found in old estates all along the eastern seaboard.
Warren F. Broderick and William Bouck, Pottery Works: Potteries of New York State’s Capital District and Upper Hudson Region (Madison, N.J.: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press; London and Toronto: Associated University Presses, 1995), p. 112.
The original mortgage from Schermerhorn to Morgan is recorded at Middlesex County, New Jersey Clerk’s Office, Mortgage Book 8, p. 367. This is an abstracted, partial transcription, which also appears in M. Lelyn Branin, The Early Makers of Handcrafted Earthenware and Stoneware in Central and Southern New Jersey (Rutherford, N.J.: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press; London: Associated University Presses, 1988), p. 98. A wonderful map of Middlesex County by J. W. Otley and J. Keily (Camden, N.J.: Published by Lloyd Van Derveer, 1850) displays the kilns, potteries, and well-known potter families in the area. It is reproduced at http://mapmaker.rutgers.edu/middlesex_county/middlesex_1850_wallmap1.jpg.
Green’s business was in northeast Philadelphia, near Second Street and Germantown Road (sometimes also listed as Franklin and School Streets). Susan H. Myers, Handcraft to Industry: Philadelphia Ceramics in the First Half of the Nineteenth Century, Smithsonian Studies in History and Technology, no. 43 (Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1980), p. 62.
Broderick and Bouck, Pottery Works, p. 112.
Heinrich Ries and Henry Barnard Kümmel, The Clays and Clay Industry of New Jersey, vol. 6, Geological Survey of New Jersey, Trenton, N.J., Final Report of the State Geologist (Trenton, N.J.: MacCrellish and Quigley, 1904).
Alvia Disbrow Martin, At the Headwaters of Cheesequake Creek (Old Bridge Township, N.J.: Madison Township Historical Society, 1979), pp. 116–24.
James R. Mitchell, “The Potters of Cheesequake, New Jersey,” in Ceramics in America, edited by Ian Quimby (Charlottesville, Va.: University of Virginia Press for the Henry Francis du Pont Winterthur Museum, 1973), pp. 319–38.
In the first quarter of the eighteenth century the Lett family intermarried with Schermerhorn cousins, making it likely that the Schermerhorn family had dealings with the Letts almost a hundred years before the potter moved to the area (if indeed he had not already been living there, or was a frequent visitor to family there).
Richard Schermerhorn Jr., Schermerhorn Family Scrapbook, LDS microfilm no. 1022390 (from original typescript), Genealogical Society of Utah, 1977, Salt Lake City.
For information regarding John P. Schermerhorn’s capacity as a soldier, establishing him in Richmond earlier than 1814, see Stuart Lee Butler, A Guide to Virginia Militia Units in the War of 1812 (Athens, Ga.: Iberian Publishing Co., 1988), p. 183.
In 1806 William Harwood was granted a patent for roofing “Tile and Pan Tile” in Richmond; Henry Leavitt Ellsworth, A Digest of Patents, Issued by the United States, from 1790 to January 1, 1839 (Washington, D.C.: Printed by Peter Force, 1840). An advertisement in the Halifax Compiler (North Carolina), June 19, 1818, p. 1, announces William Harwood’s establishment of the Petersburg Stoneware Manufactory.
July 31, 1818, City of Richmond, Va., Records No. 6, Common Council 1816–1819, p. 244, indicating a chamberlain was to pay John P. Schermerhorn $79.75 for the storage of gunpowder.
Butler, Guide to Virginia Militia Units in the War of 1812, p. 183.
For confirmation of John P. Schermerhorn’s role in the War of 1812 and pushing back to 1813 evidence of his presence in Richmond, see National Archives and Records Administration (hereafter NARA), Record Group 94, Records of the OYce of the Adjutant General, War Department, Muster Rolls of Volunteer Organizations of the War of 1812 from Virginia, Washington, D.C.; and Muster Rolls of the Virginia Militia in the War of 1812 Being a Supplement to the Payrolls (Richmond, Va., 1852), pp. 346, 790. As a point of interest, it appears Schermerhorn’s commanding oYcer, Colonel John Ambler, also owned riverfront property in the vicinity of Rocketts about this time (1815).
Enquirer (Richmond), June 25, 1814, p. 3, col. 5, and Virginia Patriot (Richmond), June 25, 1814, p. 2, col. 5. The ads detail the varieties of vessels offered and their associated prices.
Daily Compiler (Richmond), July 9, 1814, p. 3, col. 4.
Virginia Argus (Richmond), June 15, 1814, p. 3, col. 3.
December 6, 1817, Mutual Assurance Society of Virginia, vol. 55, reel 6, no. 964.
Records of 1820 Census of Manufacturing, Virginia, Henrico County, microcopy no. 279, roll 18, item 508, NARA (Washington, D.C.).
The 1820 Census of Manufacturers, Henrico County, Virginia, lists “Thomas Amos, stoneware manufactory; Samuel Frayser, Stoneware manufactory &c.; John P.Schermerhorn, Stoneware of all kinds; Samuel Wilson, stoneware of all kinds.”
Richmond Commercial Compiler, October 3, 1820, p. 3, col. 3.
Richmond Directory, Register and Almanac for 1819 (Richmond, Va.: Published by John Maddox, 1819), pp. 21, 44: “The rates for every dray or cart, shall be as follows, viz: From Rockets’ landing on the north west of Gilly’s creek to Rockets’ warehouse, 20 cents.”
George W. Bagby, Canal Reminiscences: Recollections of Travel in the Old Days on the James River and Kanawha Canal (Richmond, Va.: West, Johnston and Co., 1879), reproduced online at http://docsouth.unc.edu/bagby/menu.html; see also Mary Wingfield Scott, Houses of Old Richmond (New York: Bonanza Books, 1941).
Henrico County Land Tax Lists, 1818–1823, reel 144, Library of Virginia, Richmond.
The purchase of 101 acres by John P. Schermerhorn from Francis Wilson is recorded in Charles City Co., Va., Deed Book 7, Sept. 16, 1830, p. 466.
Henrico County Land Tax Lists, 1845–1860, reel 147, Library of Virginia, Richmond.
Henrico County Will Book 13, reel 60, March 15, 1850, p. 378, Library of Virginia, Richmond.
Compare with a three-gallon jug marked “C. CROLIUS MANUFAXTURER NEW-YORK” and three loosely defined blue swags illustrated in American Stoneware and Pottery at Absentee Auction Catalogue, sale cat. (Woodstock, Conn.: Arman Absentee Auctions, November 5, 1986), p. 11, no. 25; and an ovoid one-gallon jug with reeded neck and great bold stamp (in semicircular form) filled with blue marked “C. CROLIUS MANUFACTURER MANHATTAN WELLS NEW-YORK” ca. 1794–1838, illustrated in 3 Behrs Antique American Stoneware Catalogue 2 (Carmel, N.Y.: 3 Behrs Antique American Stoneware, 1982), pp. 55–56, fig. 181.
Compare with decorative motifs on examples pictured in Mitchell, “The Potters of Cheesequake, New Jersey.”
See Robert Hunter and Marshall Goodman, “The Destruction of the Benjamin DuVal Stoneware Manufactory, Richmond, Virginia,” this volume.
See Robert Hunter, Kurt C. Russ, and Marshall Goodman, “Eastern Virginia Stoneware,”Antiques 167, no. 4 (April 2005): 124–33.
See Mitchell, “Potters of Cheesequake”; Harold F. Guilland, Early American Folk Pottery (Philadelphia: Chilton Book Co., 1971).
See Mitchell, “Potters of Cheesequake, New Jersey,” p. 320, figs. 1b, c.
A forthcoming article by Kurt C. Russ and Robert Hunter in Ceramics in America (2006) will examine in greater detail other nineteenth-century Richmond-area potters and their role in the expanding regional industry in Henrico and Charles City counties as well as in Petersburg.
