
George Washington Felt, View of Court House Square, Salem, Massachusetts, 1810–1820. Oil on wood panel. 35" x 52". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of B. F. Brown.)
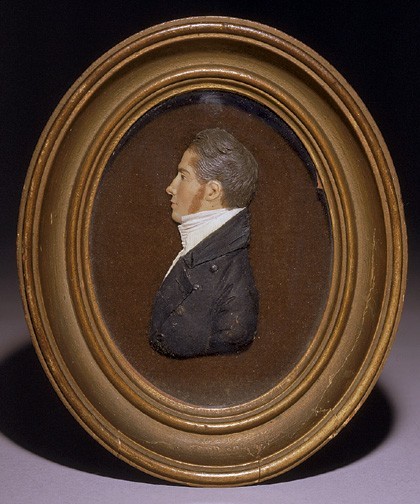

John Christian Rauschner, William Hook, ca. 1809. Colored wax. H. (frame) 6 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; photo, Mark Sexton.)

Gentleman’s secretary, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1805. Mahogany with pine. H. 96 3/8", W. 72 1/8", D. 20 1/4". (Courtesy, Museum of Fine Arts, Houston; gift of Miss Ima Hogg.)
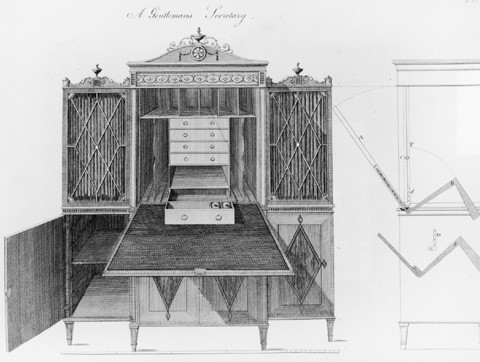
Design for a “Gentleman’s Secretary” illustrated on plate 52 of Thomas Sheraton’s The Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Drawing Book (1793). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)
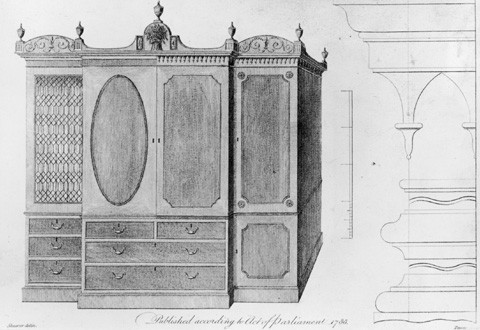
Thomas Shearer, design for a “Wing Clothes Press,” illustrated on plate 3 of the Society of Upholsterers, Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices (1788). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)
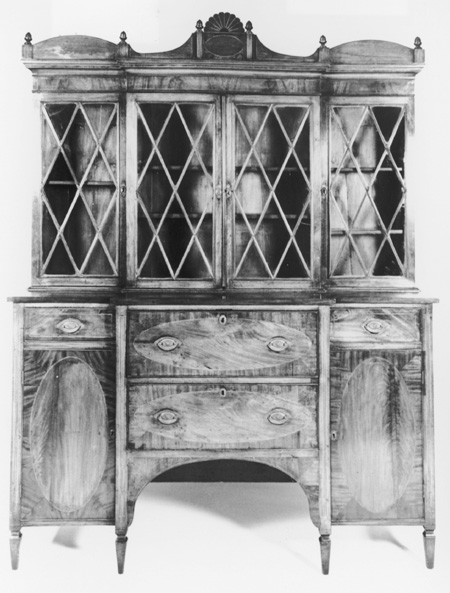

Gentleman’s secretary attributed to Edmund Johnson, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1812. Mahogany and satinwood with pine. H. 88", W. 67 1/2", D. unrecorded. (Courtesy, Sotheby’s.)

Secretary-and-bookcase, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1800. Mahogany with pine. H. 91 1/2", W. 45", D. 23". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, bequest of Mrs. Arthur West; photo, Mark Sexton.)

Secretary-and-bookcase with the label
of William Appleton, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1804. Mahogany and pine. H. 99 1/2", W. 42", D. 24 1/2". (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum.) An inlaid scroll volute similar to those on this example is illustrated in a design for a bookcase on plate 1 of the Society of Upholsterer’s Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices.
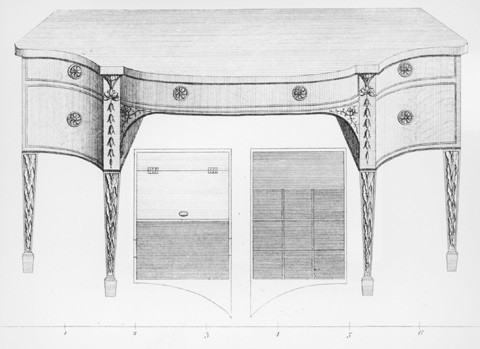
Design for a “Side Board” illustrated on plate 29 of the second edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (London, 1789). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)

Sideboard made by Daniel Clarke, Salem, Massachusetts, 1797. Mahogany with pine. H. 37 3/4", W. 68 1/2", D. 28". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, gift of Eliza and Mary Ropes; photo, Mark Sexton.) This sideboard differs from the design illustrated in fig. 9 in having a cabinet with two doors beneath the center drawer.

Sideboard bearing the label of Edmund Johnson, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1810. Mahogany with pine. H. 39 1/2", W. 63 1/2", D. 26 1/4". (Private collection; photo, Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, Winterthur Museum.)

Sideboard attributed to Nathaniel Safford, Salem, Massachusetts, 1805. Mahogany with pine. H. 42", W. 69", D. 26". (Private collection; photo, Mark Sexton.)
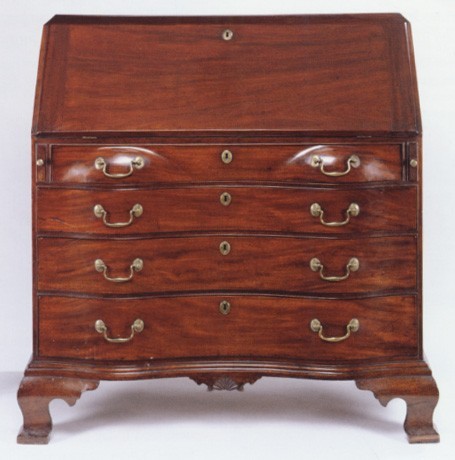

Desk attributed to Elijah Sanderson, Salem, Massachusetts, 1780–1800. Mahogany and pine. H. 43 3/8", W. 45", D. 23". (Courtesy, New England Historic Genealogical Society.)
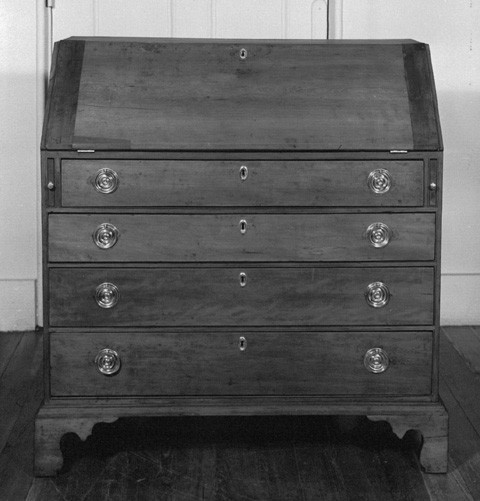

Desk by Edmund Johnson, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1800. Cherry with pine. H. 45", W. 21", D. 42 1/4". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of F. J. Bradlee.)

Dwarf clock with movement by Samuel Mulliken II, Salem, Massachusetts, 1790–1796. Mahogany with pine; brass. H. 36 3/8", W. 11 3/4", D. 7". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; photo, Mark Sexton.)
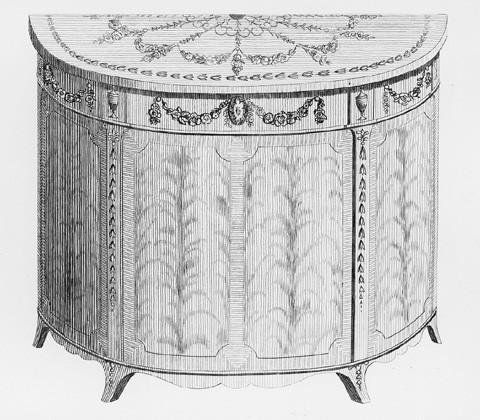

Design for a “Commode” illustrated on plate 78 of the third edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1794). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)

Commode, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1810. Mahogany with pine. H. 40", W. 55", D. 32". (Courtesy, Christie’s.)

Commode with carving attributed to Samuel McIntire, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1805. Mahogany with pine. H. 43 1/4", W. 65 3/4", D. 28 1/4". (Courtesy, Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, Winterthur Museum.)
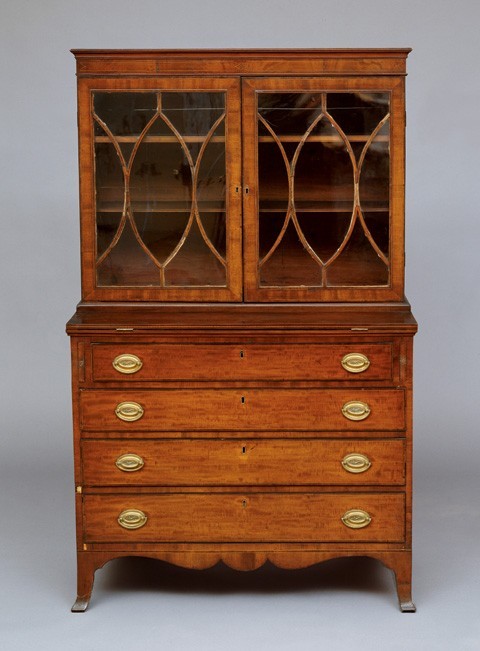

Lady’s secretary, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1810. Mahogany with pine. H. 61 1/4", W. 38", D. 29 1/4". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; bequest of Mrs. Arthur West.)
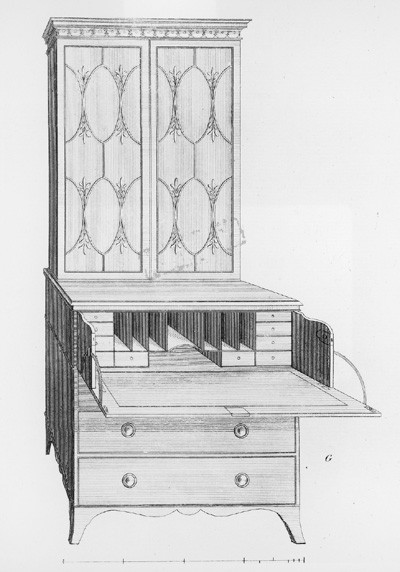
Design for a “Secretary and Bookcase” illustrated on plate 44 of the third edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1794). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)
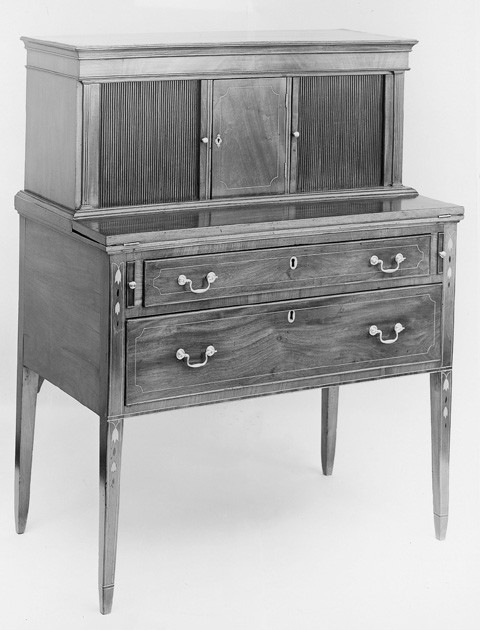

Lady’s tambour writing table by Elijah Sanderson, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1810. Mahogany with pine. Dimensions not recorded. (Courtesy, Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, Winterthur Museum.)
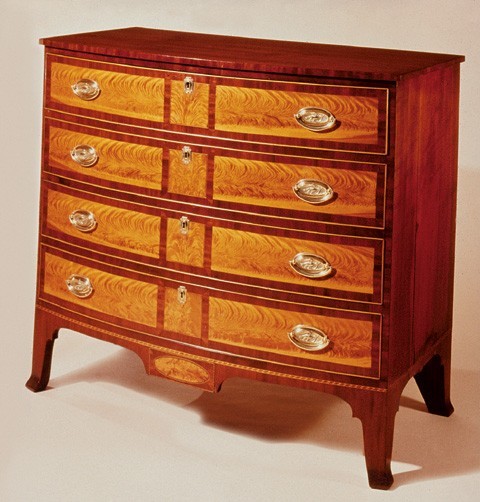

Circular front bureau, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1813. Mahogany and birch with pine. H. 37 1/2", W. 41", D. 21 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of Francis and Miriam Shaw.) The chest descended in the family of Salem merchant Aaron Waite.

Dining table, eastern Massachusetts, 1795–1815. Birch. H. 28", W. 47 1/2", D. 46". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of Charles Cotting, Jr.)
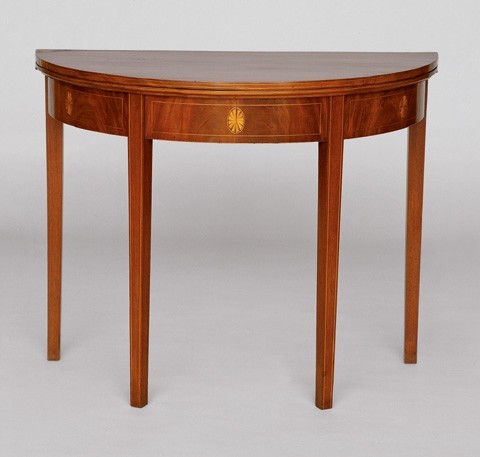

Card table attributed to William and Samuel Fiske, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1800. Mahogany with pine. H. 28 1/2", W. 35 3/4", D. 19 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; bequest of Mrs. Isabel Newcomb.)

Night table made by Elijah Sanderson, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1800. Mahogany with pine. H. 29 1/2", W. 25 3/4", D. 19". (Private collection; photo, Peabody Essex Museum.)
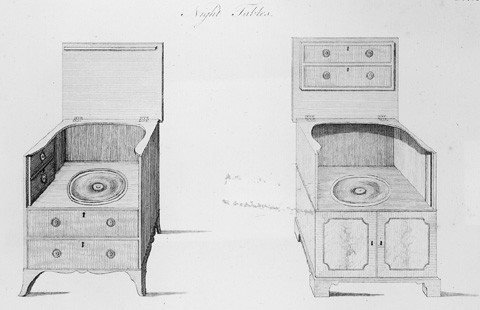
Designs for “Night Tables” illustrated on plate 82 of the third edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1794). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)

Pembroke table, possibly Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1810. Mahogany with pine. H. 28", W. 33 1/2", D. 33 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum.)

Quarter table, probably Maryland, 1795–1810. Mahogany with pine and tulip poplar. H. 32 3/4", W. 32 3/4", D. 22 7/8". (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum.)

Table, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1789. Pine; black, brown, white, and ochre paint. H. 30 1/4", W. 42", D. 22 1/4". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of Ellen Chever.)
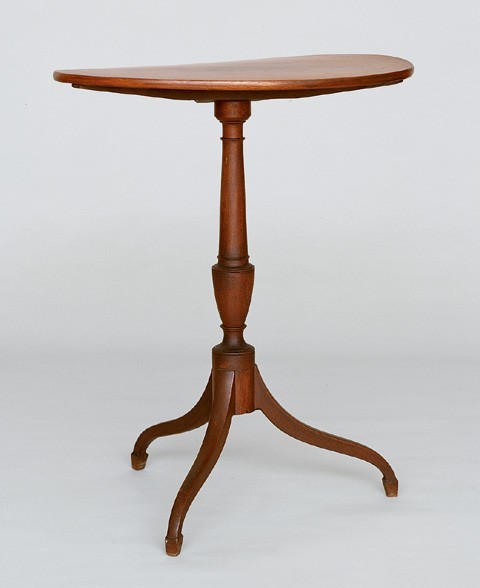

Stand, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795– 1805. Mahogany. H. 30 1/2", W. 24", D. 15 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of Mrs. George Nichols.)

Firescreen, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1805. Mahogany. H. 59 3/4", W. 17 1/2", D. 17 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; bequest of George Rea Curwen.)
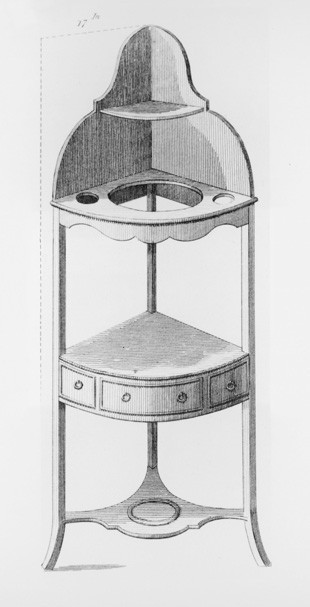
Design for a “Corner Basin Stand” illustrated on plate 42 of Thomas Sheraton’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Drawing Book (1793). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)
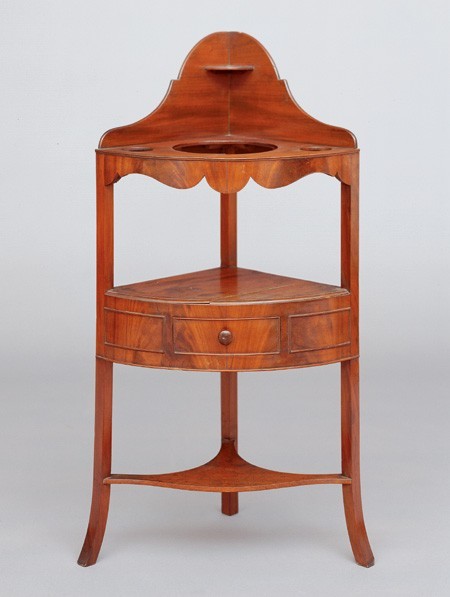

Corner washstand, Salem, Massachusetts, 1800–1815. Mahogany with pine. H. 41", W. 14 1/2", D. 14 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; photo, Mark Sexton.)

Cradles, Salem, Massachusetts, 1790–1810. (left) Mahogany with pine. H. 29", L. 40", W. 21 1/2". (right) Pine; blue-green paint. H. 31", L. 40", W. 20". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; [left] gift of Mr. and Mrs. Joseph K. Elliot.)

Sofa, possibly by Nathaniel Safford, with carving attributed to Samuel McIntire, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1805. Mahogany with unidentified secondary woods. H. 38 1/2", L. 83", D. 33". (Private collection; photo, Mark Sexton.)
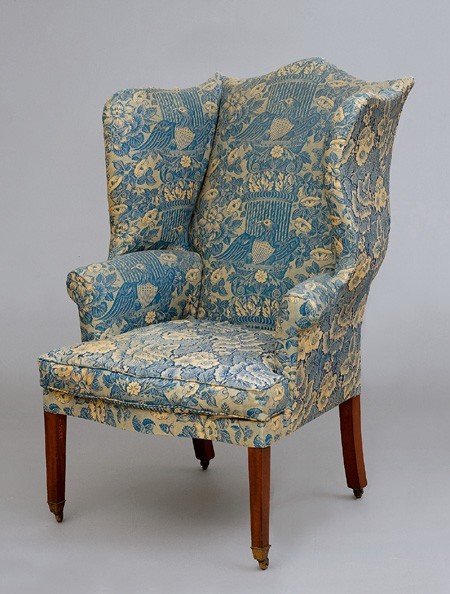

Easy chair, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1800. Mahogany. H. 48", W. 27 1/2", D. 21". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, bequest of George Rea Curwen; photo, Mark Sexton.)
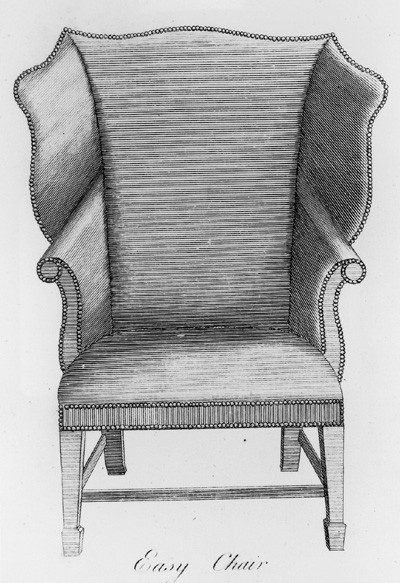
Design for an “Easy Chair” illustrated on plate 15 of the second edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1789). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)
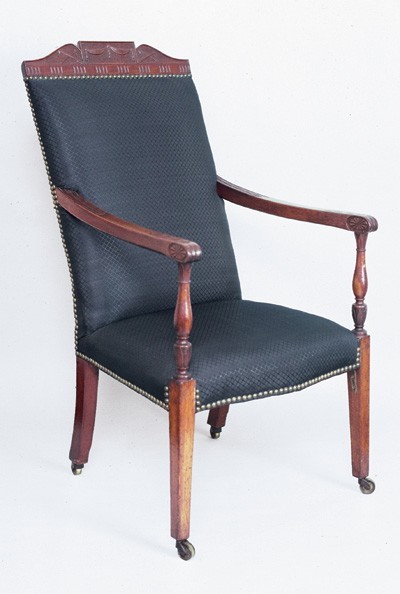

Armchair, Salem, Massachusetts, 1795–1805. Mahogany with unidentified secondary woods. H. 43 1/2", W. 23", D. 19 1/2". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; gift of George Rea Curwen.)

Lolling chair, Salem, Massachusetts, ca. 1805. Mahogany with unidentified secondary woods. H. 42", W. 24", D. 21". (Private collection; photo, Peabody Essex Museum.)

Window stool with carving attributed to Samuel McIntire, Salem, Massachusetts, 1801. Mahogany with unidentified secondary woods. H. 26", W. 44 1/2", D. 14 3/4". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, gift of the estate of Charlotte Nichols; photo, Mark Sexton.)
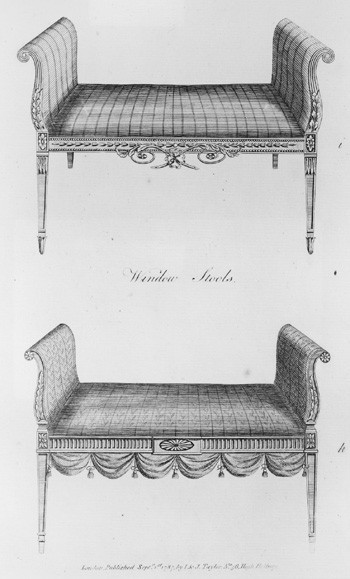
Designs for “Window Stools” illustrated on plate 19 of the third edition of George Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1794). (Courtesy, Winterthur Museum Library: Printed Books and Periodical Collection.)

Detail of a bed post with carving attributed to Samuel McIntire, 1801–1811. Mahogany. H. 76", W. 4", D. 4". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, gift of the estate of Charlotte Nichols; photo, Mark Sexton.)

Bedstead, Salem, 1795–1801. Mahogany and maple with pine. H. 87", W. 57", D. 79". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, gift of Deborah J. Elliot: photo, Mark Sexton.)

Folding cot, probably Salem, Massachusetts, nineteenth century. Maple, pine, iron, and canvas. H. 25", W. 79", D. 55". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; photo, Mark Sexton.)
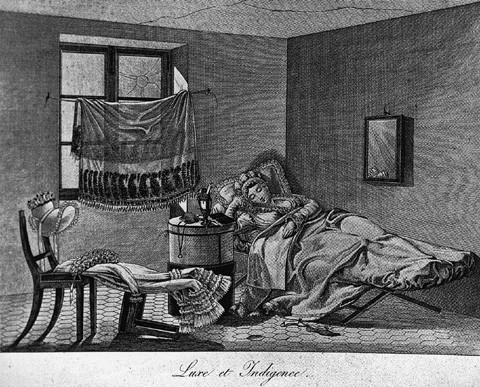
Luxe et Indigence, France, ca. 1818. Engraving. Dimensions not recorded.

Sea chest, probably Salem, Massachusetts, 1811–1830. Pine; gray paint. H. 18 3/4", W. 49 1/2", D. 18". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum, gift of the Reverend George D. Latimer; photo, Mark Sexton.) This chest belonged to Capt. Charles Hoffman of Salem.

Michele Felice Cornè, The Death of William, Salem Massachusetts, ca. 1807. Watercolor on paper. 19 1/2" x 15". (Courtesy, Peabody Essex Museum; deposit of Mrs. Nathaniel S. Sanders.) The decceased was a mamber of the Webb or Luscomb family of Salem.

Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, Associated. June 26 1801. Printed by Joshua Cushing, Salem 1801. (To scroll through all the pages click on the image.)



















In December 1999, the Peabody Essex Museum purchased an unrecorded cabinetmakers’ price book published in Salem, Massachusetts, in 1801. Titled "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, Associated June 26, 1801," the booklet is the first document to give a formal voice to one of the most important centers for furniture production during the Federal period. Since 1915, numerous scholars have attempted to chronicle various aspects of Salem’s furniture making industry, relying largely on receipts, shipping manifests, and craftsmen’s account books. Additional documentation has come from objects bearing labels or brands of owners or makers. With many aspects of work from this complex urban center yet to be explored, the "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" provides an accurate snapshot of the industry at a pivotal moment in its development and establishes a useful framework and period terminology to aid further study.[1]
The booklet contains twenty numbered pages; the first six state the twelve articles or rules governing the new society, along with the names of the sixteen founding members. The second part contains twelve pages listing various forms of furniture along with the price for making and retailing each. Seventeen other American or English cabinet and chairmakers’ price books, in either manuscript or printed form, predate the Salem example. These include price books from Providence, Rhode Island (1756), London (1788, 1793, and 1797), Philadelphia (1772, 1786, two in 1794, 1795, and two in 1796), Hartford, Connecticut (1792), New York (1796 and 1800), Hatfield, Massachusetts (1796 and 1797), and Norwich, England (1801). Each one represents an attempt either by the masters or journeymen to regulate prices and the standards of work within their craft community. Most list the rate journeymen will be paid on a piecework basis for making various furniture forms, while two list only the retail prices. A number of these agreements also established a forum to handle disputes between members. Indeed, several urban American price books were the direct outgrowth of labor disputes between journeymen and masters. As decorative arts historian Charles Montgomery noted, price books "chart a key development in the emergence of labor from its vassal-like beginnings to its present day position of power. They mark the organization of labor and document its demands, the acceptance of arbitration and reach agreement based on a piecework system for remuneration."[2]
The most influential price book was The Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices, and Designs of Cabinet Work, published in 1788 and revised in 1793 and 1803. Comprehensive in scope, it was the first to contain engraved illustrations that helped spread knowledge of London furniture forms and a common neoclassical design vocabulary. This publication had a direct influence on several other price books, including those published in Philadelphia and New York. Surviving price books from the smaller centers such as Providence, Hartford, and Hatfield are more original in their content and arrangement, reflecting more closely local preferences and practices. The "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" falls into this latter group, for it owes little to the London version or any other previously published price book. It appears to be an entirely original document accurately reflecting the needs and activities of the most prominent group of master cabinetmakers in Salem in 1801.
Like the first edition of the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices, the "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" does not list prices for chairmaking. London craftsmen maintained separate price books for cabinetmaking and chairmaking until 1802, reflecting the clear division that existed between the cabinetmaking, carving, and chairmaking trades. The absence of chairs in the Salem book suggests that a similar situation existed there, more so perhaps than in other American cities. Chairs outnumbered all other forms shipped from Salem between 1790 and 1810. The few surviving documents relating to the town’s chairmaking industry, however, provide no evidence of any formal organization or price list. Nevertheless, historical references document business relationships between chair makers and cabinetmakers. Some cabinetmakers bought chairs for inventory or took them as consignments for venture cargo shipments. Elijah and Jacob Sanderson, for example, formed a partnership with cabinetmaker Josiah Austin and purchased painted seating from the Burpee Chair Manufactory, Micaiah and Edward Johnson, Isaac Stone, and James C. Tuttle.[3]
By 1801, Salem merchants had successfully revived the town’s maritime economy by establishing new trade routes to the Far East. With unprecedented profits resulting from daring voyages to uncharted territories, Salem’s merchant class ushered in an era of unsurpassed prosperity that transformed the community. There was a dramatic increase in opportunities for employment as local industries expanded, especially in the areas of shipbuilding, house construction, and furniture making. Artisans came from surrounding communities, more distant coastal towns, southern New Hampshire, and a few were natives of England and Ireland. Furniture historian Margaret Clunie documented only three cabinetmakers active in Salem between 1770 and 1780, but by 1801 there were at least twenty-one. A majority were born and trained elsewhere, including most, if not all, of the members of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society. They were part of a town population that had grown by 1800 to just under ten thousand inhabitants, making Salem the sixth largest city in the United States.[4]
This expansion coincided with the introduction of the "antique" or neoclassical taste in architecture and furniture. The style received its first significant expression in 1793 with the construction of the Nathan Read house designed by Salem architect and carver Samuel McIntire. At least six other three-story townhouses were built during the next eight years. Newly arrived cabinetmakers and chair makers found work furnishing these residences as well as public buildings constructed during the same period. A view of the center of town painted about 1810 (fig. 1) provides an image of this prosperity, showing a number of the new buildings along Court Street (now Washington Street) where cabinetmakers Samuel Frothingham, Samuel Cheever, and many of their contemporaries lived and worked. There were also opportunities to supplement local custom orders by producing furniture for the burgeoning venture cargo trade. Rev. William Bentley observed that many of these artisans had attained "wealth by other means than the slow gains of its [native born] inhabitants." Shipping manifests listing furniture transported from Salem rose from ?ve in 1789 to forty in 1800, the most in a given year. By the turn of the century, the industry had reached a point where some attempt at regulation was desirable.[5]
The establishment of the Sanderson-Austin partnership in 1779 was a watershed in the development of Salem’s furniture export trade. The firm employed many cabinetmakers, journeymen, and apprentices, as well as carvers, gilders, turners, and upholsterers on a piecework basis. They sent large shipments of furniture on speculation to the southern states, the East and West Indies, the Madeiras, South America, Africa, and more distant ports, including those in India. Not surprisingly, the names of all three men appear at the top of the list of the founding members of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, a clear indication of the central role they must have played in forming that organization.[6]
Although all of the other cabinetmakers on the list appear to have operated their own shops, many were relatives, former employees, or associates of Austin and the Sandersons. Richard Austin was Josiah’s brother and Daniel Clarke was a nephew and former employee of the Sandersons. William Hook (fig. 2), the youngest member of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, came from Salisbury, Massachusetts, and worked for both Jacob Sanderson and Edmund Johnson before setting up his own shop in 1800. The names of many other members appear in the Sandersons’ business records from the 1790s, underscoring the cooperative rather than competitive nature of the town’s cabinetmaking trade.[7]
Salem artisans often joined forces to purchase materials, assemble large venture cargos, and share the cost and risk of shipping. In 1795, George W. Martin, William Appleton, Josiah Austin, and the Sandersons bought a large quantity of mahogany and hired Col. Israel Hutchinson to cut the logs into planks. The following year, the Sandersons, Austin, and William Appleton purchased the schooner Olive Branch, undoubtedly for use in the furniture export trade. Most cooperative efforts involved venture cargo, such as Daniel Clarke, Edmund Johnson, Nehemiah Adams, and Josiah Austin’s shipment of furniture to Surinam in 1799.[8]
This cooperative and entrepreneurial spirit led to the founding of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society in June of 1801. The governing rules were simple, straightforward, and democratic. Membership was open to anyone "generally accepted" to be a "master-cabinet-maker"—a designation determined by a vote of the entire membership. The society met in March, June, September, and December. Missing a meeting, tardiness, neglecting to bring one’s copy of the price book, and failure to adhere to set prices were offenses punishable by fines. It was the clerk’s duty to record any changes agreed upon by vote directly into each member’s book. Anticipating this practice, Joshua Cushing left a generous space between each entry when he printed the book. In the copy illustrated here, clerk Daniel Clarke recorded the first change on September 22, 1801, when the society voted to make the fine for deviating from the prices the cost of making the piece of furniture.[9]
The other articles in the price book established arbitration procedures to settle potential grievances between members and between masters and their apprentices. Members were required to report any apprentice attempting "to leave his master or in any manner to injure him" and were forbidden from harboring runaways. Court cases and newspaper notices indicate that disputes over apprentices were a persistent, albeit infrequent, problem. In 1798, Elijah Sanderson sued B. Radson for causing one of his apprentices to leave. Three years later, Edmund Johnson offered a thirty-dollar reward for information leading to the return of two nineteen-year-old apprentices. He warned all persons against "harboring or trusting said runaways" and cautioned "masters of vessels…against carrying them to sea as they would avoid the penalty of the law." The time invested in training apprentices and the cost of housing, feeding, clothing, and educating them was considerable. Rewards typically varied depending on an apprentice’s skill and time served.[10]
The last twelve pages of the "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" list the retail and journeyman’s prices for thirty different furniture forms, half of which were available with less expensive woods, design features, and ornamental details. With only sixty-four separate entries, the price book documents a narrow range of neoclassical forms popular within the community. It is much smaller than the Philadelphia and London publications, both of which have 346 entries.
Evidence suggests that Salem tradesmen and consumers began embracing the neoclassical style during the last quarter of the eighteenth century. Bookseller John Jenks, for example, advertised the first edition of George Hepplewhite’s The Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1788) in 1791. Designs from this book, the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices, and Thomas Sheraton’s The Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Drawing Book (1793) clearly influenced Salem production. Some of the newer forms illustrated in these publications—sideboards, window stools, commodes, and washstands—are mentioned in the Salem price book, whereas many others are not. Conspicuously absent are references to work tables, chamber or dressing tables, drawing tables, pier tables, mixing tables, urn stands, bidets, knife boxes, dressing boxes, tea caddys, trays, bottle boxes, and other forms known to have been made in the city.[11]
Documentary evidence suggests that Salem furniture makers made few of the aforementioned objects prior to 1801. Margaret Clunie’s survey of 109 shipping manifests submitted between 1790 and 1810 lists twenty-two forms that generally match entries in the price book but makes no mention of a "work table." The earliest use of that term in Salem is August 1807, when the Sandersons paid Samuel McIntire three dollars for "Reeding & Carving 4 legs for [a] Worktable." During the eighteenth century, few American cabinetmakers attempted to compete with their British counterparts in the manufacture and sale of looking glasses, dressing boxes, and other objects with mirrored components. The first reference to a dressing box being made in Salem is 1809.[12]
The retail price of objects listed in the "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" is between three and three-and-one-half times the cost of making the piece. Research by Charles Montgomery suggests that large cabinet shops in other urban centers evidently worked on similar profit margins during the early nineteenth century. Labor determined most of the cost. As the price book reveals, a card table that retailed for fourteen dollars required approximately four days of labor at one dollar per day.[13]
The society clearly monitored the prices of all objects commonly produced by its members and on several occasions altered them. Ink notations in the Peabody Essex copy record the lowering of prices for the mahogany chair frame and press bed in December 1801 and for an easy chair frame, fire screen, and wash stand in June 1802. The largest number of changes was voted at the September 1802 meeting, when the society agreed to offer a fully painted cradle for six dollars and lowered prices for the larger "secretary & bookcase" and all variations of the bureau and lady’s secretary. These forms were among the most popular export items, but there is no indication of what prompted the changes. The last changes recorded in the book occurred on December 6, 1803, when the members voted to raise the price of several bedsteads and to add a pembroke table and coffins to the list.
The brevity of the entries for each form is unusual, especially when compared with those in contemporary price books, which usually describe material, structural, and decorative options and the cost for each. It is possible that the society’s members were so familiar with each other’s work and the demands of their consumers that it was unnecessary to include too much detail. During the late eighteenth century, Salem cabinetmakers almost invariably used square tapered legs for tables, whereas their counterparts in other American cities and London had a more varied repertoire. The earliest reference to turned and reeded legs in Salem is 1803.[14]
Entries for certain forms allude to the specialization that existed in Salem’s furniture making community. Carving was "excluded" from the price of the sofa, mahogany chair, window stool, and bedstead with "swelled pillars," which implies that the patron determined the type and amount of ornament, and that most cabinetmakers subcontracted carving to specialists. The same was true of "painting." This generic reference probably encompassed a variety of treatments including faux surfaces, trompe l’oeil, and gilding. The terms "superior quality," "best quality," and "another quality" are more difficult to access, but in some instances they also refer to decoration. The "superior quality" cabinet, for example, was "inlaid and decorated in every part" and had an elaborate "checkered cock bead round the doors."
All of the entries in the "Articles of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society" are transcribed below. Each has been numbered to simplify future reference and annotated to establish the cultural, historical, and artistic context of the form described.
PRICES of FURNITURE, and JOURNEYMEN’S PRICES for MAKING, established by the Society June 26th, 1801:—To be altered at the discretion of the Majority.
[1] CABINET, of a superior quality, with circular doors, inlaid and decorated in every part, to be
made with a cock bead round the doors, drawers
and head———dolls. 120
Making———dolls. 40
[2] Ditto, finished with circular doors———115
Making———37
[3] Ditto, of another quality, with diamond doors———110
Making———34
The first three entries describe a "cabinet" or gentleman’s secretary, the most expensive form in the price book and one long associated with Salem. More than a dozen examples have survived including one of "superior quality" with husks, stringing, and "check’d" inlay (fig. 3). An amendment at the end of the price book notes that the term "check’d" should precede "cock bead" in the first entry.[15]
Although no European prototype for the archetypal Salem cabinet is known, several features typical of this form have parallels in British design books. The lower section (see fig. 3) is similar to that of a gentleman’s secretary illustrated on plate 52 of Sheraton’s Drawing Book (fig. 4), whereas the pediment resembles that of a "wing" clothes press shown on plate 3 of the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices (fig. 5). Gothic cornice moldings related to the one shown in the latter engraving also occur on Salem "cabinets" and other case forms.[16]
The term "circular doors" in the first and second entries probably refers to curved glazing bars like those on the upper doors of the gentleman’s secretary illustrated in figure 3, rather than oval panels of veneer like those on the lower doors. This glazing pattern appears on a group of doors illustrated on plate 27 in the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices. The term "diamond doors" in the third entry refers to the crossed glazing bars found on many Salem examples, including one with a pediment very similar to that shown in the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices (fig. 6).
The earliest documented Salem gentleman’s secretary was made by Nehemiah Adams before 1798. Because of their high cost, these forms are rarely found in venture cargo manifests. Elijah Sanderson shipped "two cases Containing One cabinet...$250" to Batavia in 1804, and William Appleton exported "two cases...[containing] one cabinet...$120" in 1805. A few of the cabinets mentioned in period documents may have been library bookcases, although only one Salem example is currently known.[17]
[4] WARDROBE, of the best quality, scrole
head, 70
Making———18
[5] Ditto, of another quality, with square
head, 60
Making———17
No Salem wardrobe from the Federal period is known, which suggests that high chests and chest-on-chests were the preferred forms for storing clothes. Most American examples are from cities and towns in the Middle Atlantic region and the South. Their popularity in the South, which was a major venture cargo destination for Salem cabinetmakers and merchants, may explain why the wardrobe form is listed in the price book. The terms "square head" and "scrole head" refer to plain and broken-scroll pediments respectively.[18]
[6] SECRETARY & BOOK-CASE, best quality, with a swell’d front———70
Making———23
[7] Ditto, of the best quality, with straight front, scrole head, crossband doors, decorated with dentals, &c———63
Making———19
[in ink] Voted Sept 21st 1802———60
[Making]———18
[8] Ditto, straight front, with pediment head, 60
Making———18
Secretary-and-bookcases were among the most popular furniture forms made in Salem. With its "swell’d front," "scrole head," carved volutes, and urn ornament, the example illustrated in figure 7 is more elaborate than any of the variants described in the price book. The façade of the secretary drawer is embellished with an applied astragal molding (or "bead") forming a rectangle with ovolo corners, a detail found on the doors and drawers of case pieces shown in many British design books (see fig. 5). String-inlaid versions of this design are even more common on Salem furniture. A secretary-and-bookcase bearing the label of William Appleton (fig. 8) represents the "straight front" form described in the second entry. The frieze decoration, consisting of interlaced stringing with a central diamond motif, occurs on case pieces by several different Salem cabinetmakers. A small secretary-and-bookcase attributed to William Appleton (Peabody Essex Museum) is a good example of the less expensive "pediment head" form. Lacking any decoration, it has lozenge-shaped door mullions and a simple pediment with plinths.[19]
[9] BOOK-CASE, with scroll head and glass doors, 28
Making———8
No Salem bookcase matching the description in the price book is known, nor do any references to "bookcases" appear in shipping manifests other than as the upper unit of a cabinet, secretary, or desk. Cabinetmaker Mark Pitman made two sets of grain-painted bookcases with "square" or "pediment" heads and glass doors on the upper and lower cases (Ropes Mansion, Peabody Essex Museum). Harvard divinity student Joseph Orne paid Pitman twenty-four dollars for making the earlier set on February 17, 1816.[20]
[10] SIDE-BOARD, sash-corner’d, with a secretary drawer, decorated, crossbanded and finished, 60
Making———18
[11] Ditto, scolloped front, with a secretary drawer, decorated and finished———57
Making———17
[12] Ditto, scolloped front, without a secretary drawer, decorated and finished———50
Making———15
The 1788 edition of Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide was the first British design book to illustrate sideboards (fig. 9), but the form was fashionable in London earlier. Like virtually all of their American counterparts, Salem cabinetmakers did not begin producing sideboards until after the Revolution. The earliest reference to the form is November 1797, when Daniel Clarke charged Nathaniel Ropes eighteen pounds for a mahogany example with a serpentine or "scalloped front" (fig. 10). Later Salem sideboards (fig. 11) typically have stringing, husks, and other inlaid motifs, and some are fitted with a secretary drawer, an unusual feature mentioned in all three sideboard entries in the price book. Sideboards with "sash corners" had additional drawers and were slightly more expensive than those with serpentine fronts. Salem cabinetmaker Nathaniel Safford made one of the former (fig. 12) for John and Elizabeth Gardner in 1805.[21]
[13] DESKS, swelled, the front and fall finiered, 40
Making———13
[14] Ditto, swelled, solid front———40
Making———11
[15] Ditto, straight front, the front, fall, top and seatboard finiered———30
Making———9
[16] Ditto, straight front and solid———30
Making———8
[17] Ditto birch, straight front———15
Making———7.50
[in ink] birch Desk———18
[18] Ditto, travelling, of the common quality, 7
Making———2
After chairs, desks were the most numerous form exported from Salem. The term "swelled" in the first two entries probably refers to the shape described today as "oxbow." Desks with shaped façades typically had fall fronts. Salem cabinetmakers made them well into the nineteenth century, even though fall-front forms were less fashionable than case pieces with secretary drawers. A desk attributed to Elijah Sanderson (fig. 13) conforms to the description in the initial entry, although the price book provides no information on the design of the foot. This is perplexing given the price difference between straight bracket, ogee, and claw-and-ball feet. Veneering (presumably in mahogany) added to the cost, whereas the use of native woods reduced it. The straight-front desk with veneered façade, fall, top, and seatboard (floor of the writing compartment) cost twice as much as a comparable form in birch. Although the only native wood mentioned in the desk entries is birch, Salem cabinetmakers occasionally used cherry. A simple cherry desk bearing the label of Edmund Johnson (fig. 14) is representative of the "gentleman’s writing desks" mentioned in many shipping manifests. The last and least expensive entry is for traveling desks. The only surviving example (Peabody Essex Museum) is a simple box with brass carrying handles, a slanted lid, and storage compartment partitioned for bottles and writing implements. Mark Pitman charged Elizabeth Ropes eight dollars for it on June 6, 1812.[22]
[19] CLOCK-CASE, mahogany, glazed and ?nished, 30
Making———9
This entry probably refers to a "Roxbury case," a modern designation for the type commonly found with movements marked by the Willard family of Grafton. Most of these cases have brass fluted quarter-columns on the waist and a hood with pierced fretwork and three plinths.[23]
A dwarf clock owned by Captain Henry Prince is the only documented Salem clock made between 1790 and 1820. It has a movement marked by Samuel Mulliken II (1761–1847), who worked in the town from 1790 to 1796 (fig. 15). His sister Mary married Elijah Sanderson. Mulliken probably made movements for cases by his brother-in-law and many of Elijah’s contemporaries. Although a few watchmakers worked in Salem during the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, no other clockmaker is recorded in Salem until the 1820s.[24]
Salem cabinetmakers clearly produced tall clock cases for local patrons as well as for the export trade. In 1795, Daniel Clarke charged "4-15-0" for "making 2 clock cases and turning the moldings for same." Eight years later, Elijah Sanderson shipped several cases with eight-day movements to Brazil. Most eight-day movements in such clocks were British or comprised of imported parts assembled by regional clockmakers. Jacob Sanderson purchased a "warrented Patent time piece" from Simon Willard in 1804 and three clocks from Levi Hutchins in 1807.[25]
[20] COMMODE, common circular, five feet in length, 60
Making———20
[21] Ditto, different sizes, in proportion
Hepplewhite’s design for a demi-lune commode (fig. 16) served as the inspiration for several Salem examples. Some have drawers and cabinets arranged like those in the engraving (fig. 17), whereas others have a different configuration. The most elaborate Salem commode (fig. 18) has four graduated drawers, the top of which has carving attributed to Samuel McIntire. In 1802, Jacob Sanderson charged Captain John Derby sixty dollars for making a "mahogany Commode with secretary draw" and an additional twelve dollars to pay "Mr. Fuller’s bill for varnishing." Salem inventories indicate that commodes were used in bedchambers for the storage of linens. Many have sliding trays rather than shelves to facilitate this function. In 1799, the appraisers of Elias Hasket Derby’s estate listed a "mahogany Commode" valued at fifty dollars in his best second-floor northwest bedchamber and noted that it contained a "Damask Table Cloth & 18 Napkins" of equal value.[26]
[22] LADY’S SECRETARY, with a frieze, head-moldings, and bracket feet———35
Making———11
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———30
[Making]———10
[23] Ditto, with legs, decorated and finished, 30
Making———9.50
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———25
[Making]———8
Given the variety of small writing desks made in Salem during the Federal period, it is surprising to find only these two brief entries for this form. The distinguishing features are the hinged fall and two sliding supports that form the writing surface when open. The retail cost of each lady’s secretary is exactly one-half that of the larger secretary-and-bookcases discussed earlier. A lady’s secretary that descended in the West family of Salem (fig. 19) has "head-moldings" and "bracket feet" (undoubtedly a reference to what are today called "French feet"), two details mentioned in the first entry. The door mullions and skirt and foot shape may have been inspired by a design for a "secretary and bookcase" in Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (fig. 20). Several Salem secretaries conforming to the description in the second entry are known. The most common variant has three drawers in the lower section and short tapered legs.[27]
The lack of references to tambour doors is surprising since they are common on Salem secretaries, particularly the type described in the second entry. Also called writing tables or tambour tables, this form was fashionable in Salem by 1797. A desk with the branded initials of Elijah Sanderson illustrates one of the most common designs with a solid central prospect door and cabinets on either side (fig. 21). Shipping manifests frequently list lady’s secretaries. Jacob Sanderson sent six valued at $243 to the Madeiras and the West Indies in 1806.[28]
[24] BUREAU, with canted corners, of best quality, finiered, decorated and crossbanded, 27
Making———9
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———25
[Making]———8
[25] Ditto, with a scolloped front, and
decorated, 25
Making———8
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———24
[Making]———7/50
[26] Ditto, with a circular front, and
decorated, 25
Making———7
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———23
[Making]———6/50
[27] Ditto, with straight front, and
decorated, 20
Making———5.50
[in ink] Voted Sept 7th 1802———18
[Making]———5
[28] Ditto, birch———11
Making———5
[in ink] Voted Sept 21st 1802———10
[Making]———5
Chests of drawers with canted corners were popular in Salem by the 1780s. Six examples made between 1785 and 1800 have ogee feet related to those on a magnificient chest-on-chest made for Elizabeth Derby West in 1796. One is completely in the rococo style, but the others have a modicum of neoclassical details. A chest in a private collection has a case and top with a modest cant, straight bracket feet, and a simplified inlaid decoration characteristic of later work. More numerous are examples of "scalloped" or serpentine-front bureaus, including one with straight bracket feet and the label of Thomas Needham. Many circular or bow front chests have also survived. A mahogany and birch veneered chest (fig. 22) that descended from merchant Aaron Wait of Salem is a sophisticated interpretation of the drop-panel form usually associated with Portsmouth. Waite was a frequent client of the Sandersons. In 1796, he paid them twenty-five dollars for a "mahogany Buro."[29]
[29] DINING-TABLES, by the set, to be 4 1/2 feet wide, and to spread 8 feet in the square, with two semi-circular ends of 2 feet in width, which adds 4 feet to the length—the spreading of the whole extent to be 12 feet in length, and 4 1/2 in breadth———60
Making———12
[30] Other sizes to be regulated in proportion.
[31] Ditto, common kind, spreading 4 feet square, 14
Making———3
[32] Ditto, birch, spreading 4 feet square———7
Making———3
No documented Salem dining tables matching the first description have been identified, but they are mentioned in both three- and four-part forms in shipping invoices. On January 18, 1802, Jacob Sanderson sent "one sett mahogany dining tables varnished, four tables in the sett" valued at $116 to the West Indies on the brig John. Approximately seven years later, Elijah Sanderson exported a set of three tables valued at fifty-five dollars on the brig Venus. A drop-leaf table that descended in the Cotting family (fig. 23) conforms to the description in the last entry.[30]
[33] CARD-TABLE, of the best quality, sash-cornered———14
Making———4
[34] Ditto, of best quality, circular, 12
Making———3.33
[35] Ditto, birch, or pine without painting———4
Making———2
During the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, Salem cabinetmakers made vast numbers of card tables for the local market and for export. Although the entries in the price book list only two shapes—"sash-cornered" and "circular"—furniture historian Benjamin Hewitt’s study of card tables suggests that Salem cabinetmakers produced a variety of "square" tables as well as examples with elliptic fronts and serpentine ends. The first entry refers to a square table with ovolo corners, a shape Sheraton called "sash plan corners." A card table bearing the label of Thomas Needham (Yale University Art Gallery) is a conservative interpretation of this form.[31]
Most documented Salem card tables have panels of contrasting veneer on the skirt. An oval set within a mitered panel is one of the most common treatments. Salem craftsmen also used patterned inlay on the edges of the leaves and skirt. Round card tables inlaid with an oval fan or patera in the center of each section of the apron were especially popular between 1795 and 1800. This treatment appears on several tables made by Samuel and William Fiske (fig. 24) and a table made by member George Whitefield Martin, while in partnership with Robert Choate in Concord, New Hampshire. In 1796, the Sandersons charged Aaron Waite of Salem twenty-four dollars for a pair of round card tables "with in Laid work."[32]
As the last entry indicates, painted tables cost one-third the price of a mahogany table. In 1808, Thomas Hodgkins charged $2.50 for "making a pine card table" for Jonathan Prince. Specialists such as William Gray and William Luscomb did the decorative painting. The latter charged Capt. Jacob Sanderson "0-9-3" for "painty a Card Table" in November 1801.[33]
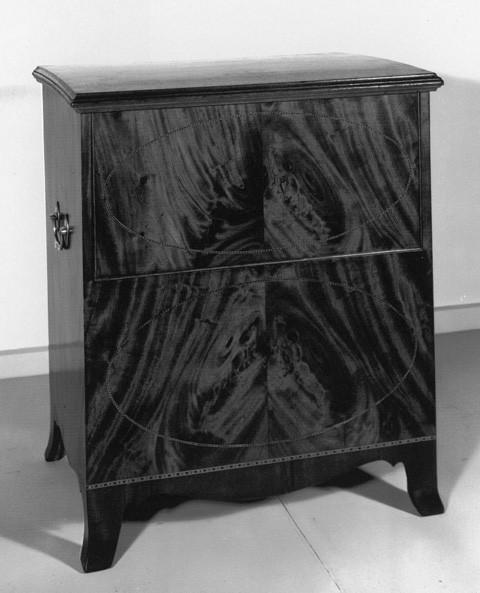
[36] NIGHT TABLE, of the common kind, 2 feet 4 inches high, and 2 feet deep, without the pan ———12
Making———4
Both Hepplewhite and Sheraton illustrated designs for night tables—small cabinets designed to conceal a chamberpot, basin, or pan. The more elaborate examples also contain compartments for a wash basin and other toiletries. A night table bearing the initials of Elijah Sanderson is one of the few documented Salem examples (fig. 25). Its dimensions are similar to those in the entry, and its form conforms to the description "common kind." The folding lid, which consists of two hinged panels, resembles the one on the right in plate 82 of Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (fig. 26). In 1808, Thomas Hodgkin charged four dollars for making "a corner night table" for the Sandersons.[34]
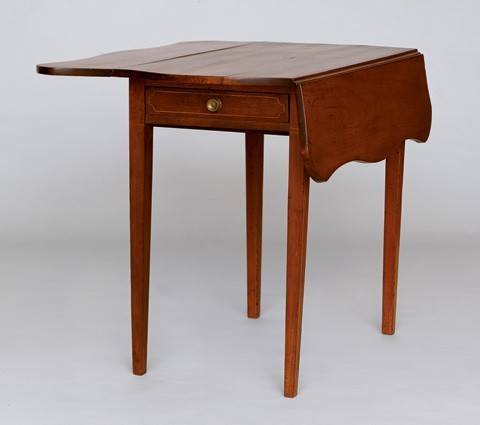
[37] [in ink] Dec 6th 1803
Voted Pembroke Tables 3 ft long & be $14
It is unclear why pembroke tables were not included in the initial printing of the price book. Small tables with folding leaves were popular much earlier, although some may have been referred to as "square," "breakfast," "folding," "leaf," or "tea" tables. An early example (Winterthur Museum) has several labels of Elijah and Jacob Sanderson. Its serpentine top and fluted Marlboro legs suggest a date in the 1780s; however, Charles Montgomery speculated these features may have remained an option through the end of the century. The neoclassical table illustrated in figure 27 has a similar top, tapered legs, and string-inlaid drawer. This model is probably more representative of the price book entry than the Sanderson example. In 1802, Capt. John Derby purchased a veneered pembroke table from Jacob Sanderson for fourteen dollars.[35]
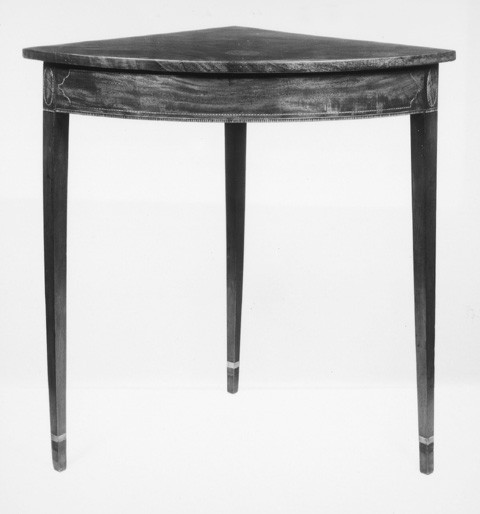
[38] QUARTER-TABLE, of the best quality, decorated, 19 inches demi-circular———6
Making———1.50
This entry probably describes a small corner table similar to the one illustrated in figure 28. Such tables were designed to fit snugly into the corner of a room and used for a variety of household functions including serving food and beverages. The cost cited in the price book is half that of a round card table. No Salem quarter-tables are known, but other triangular forms—corner sideboards, washstands, and night tables—are relatively common.[36]
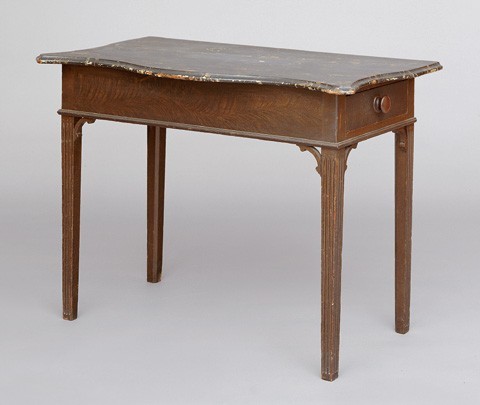
[39] SLAB-TABLE, without painting———3
Making———1
Although the period term "slab table" generally refers to a rectangular table with a marble top, the amounts cited in the price book indicate a different form, possibly a simple folding table or an ironing board. An object conforming to this entry is described in the Cabinet-Makers’ London Book of Prices under dining tables: a "four foot flap or slab, the top 3 inches wide, hung with a rule joint to the flap. With 2 fram’d brackets to support ditto, to fix against a wall." The kitchen in Elias Hasket Derby’s mansion had a "folding board" valued at three dollars in 1799, and John Chandler charged Aaron Waite three dollars for "Making a folding board" in 1813. Waite’s folding board was probably an ironing board, since Chandler billed him for "two closehorses" and a number of small kitchen items at the same time.[37]
A few Salem tables with faux marble tops are known including a pier or dressing table used by George Washington at Joshua Ward’s home in 1789 (fig. 29). The top has a realistically marbleized surface and the frame and legs are grain-painted to imitate mahogany. In 1790, Salem painter William Gray painted a table "marble" for Joseph Sampson. Approximately six years later, he charged Dr. Edward A. Holyoke "1-25-0" for "painting a table mahogy & marble."[38]
[40] KITCHEN TABLE, with a drawer———3
Making———1.50
Many common kitchen tables from the early nineteenth century survive, but no documented Salem example is known. Most kitchen tables found in or near the town are pine and maple and have an overhanging rectangular top with "bread board" ends, square tapered legs with beaded edges, and a single drawer with a wooden pull. The frame and legs are usually painted, but the top is often left unfinished. Inexpensive tables were among the most popular export items.[39]
[41] STAND, mahogany, oval, to turn up———5
Making———1.50
An oval-top candlestand that descended in the Peirce-Nichols family of Salem (fig. 30) is one of the most successful interpretations of this popular form. It is attributed to Salem based on its history and the similarity of its pillar to that on an earlier stand by William King. Several more elaborate candlestands with satinwood veneer and "check’d" inlay may also have been made there. Evidence suggests that Salem cabinetmakers routinely purchased pillars for stands and other three-legged forms from turners. The Sandersons purchased turned "stand pillars" from Jonathan Gavet and Daniel Clarke in 1801. The following year, Clarke charged them twenty-five cents for a single pillar.[40]
[42] FIRE-SCREEN, of the common kind———8
Making———2
[in ink] Voted June 1st 1802 without flap leaf———7.5
[Making]———1.6
Several Salem fire screens with a folding shelf or "flap leaf" to support a candlestick survive. The shield and shelf usually have a brass ring with a tension clip that engages the pole and allows the user to adjust the height. The example illustrated in figure 31 probably pre-dates the price book. It has pillar turnings similar to those on a candlestand made by John Gavet in 1784.[41]
On December 24, 1802, Jacob Sanderson paid Thomas Hodgson two dollars for making a fire screen. Three days later, Sanderson charged John Derby eight dollars for the same piece, which he described as a "Fire Screen with a leaf to sett candlestick on." Plate 93 of Hepplewhite’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide illustrates designs for three "Pole Fire Screens," one with a "pillar-and-claw" base similar to the example shown in figure 31.[42]
[43] WASH-STAND, circular, of the common kind, 9
Making———3.50
[in ink] Voted June 1st 1802———8
[Making]———3
[44] Ditto, square———6
Making———2
The first entry refers to a corner basin stand, an object Hepplewhite considered "very useful...as it stands in a corner out of the way." Sheraton also published designs for this form (fig. 32), one of which resembles an example (fig. 33) Lydia Kimball received from her uncle, Captain Joseph White. Although the maker of her stand is not known, similar ones are documented to Salem cabinetmakers Nehemiah Adams and William Hook.[43]
The stand mentioned in the last entry was probably neoclassical in style, but square basin stands were fashionable decades earlier. Hepplewhite published three variations on plate 84 of the Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide, two with a lower shelf and drawer and one with a cabinet and drawer. The designs on the right and left have folding lids to conceal the basin, a feature found on one example attributed to Salem.[44]
During the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, the terms "basin stand" and "wash stand" were used interchangeably. Lydia Waite purchased "1 bason stand" for "2-8-0" from William Appleton in 1796. Six years later, the Sandersons began exporting "wash hand stands," although they do not appear to have been in great demand as venture cargo until 1810. Like some of their contemporaries, the Sandersons purchased certain components for these forms from specialists. Turner Jonathan Gavet sold them parts for washstands in 1801.[45]
[45] CRADLE, mahogany———12
Making———3
[46] Ditto, cedar———8
Making———3
[47] Ditto, pine, without painting———4
Making———1.5
[in ink] Voted Sept 21st 1802 painted complete———5
The board cradles illustrated in figure 34 were probably made in Salem about the same date, given the similarity of various design and construction features. The more elegant mahogany example descended from George and Elizabeth Leach Watson who were married on June 14, 1801. On both cradles, dovetails join the footboard to the sides, whereas nails secure the bottom, rockers, and elements of the hood. The double-arch treatment on the side of each hood is identical, and both sets of rockers end in a modified volute. The Watson cradle retains its brass carrying handle on the footboard and back of the hood, a convenient feature no longer on the pine example. Entries in the price book suggest that the pine cradle cost half as much as the mahogany one.
[48] SOFA FRAME, with a mahogany top-rail, excluding the carving———22
Making (the moulding to be finished)———6.50
[49] Ditto, without mahogany top———20
Making———5
Most documented Salem sofas contemporary with the price book have scrolled arms and serpentine or "commode" backs. Similar features are shown on sofas in eighteenth-century design books including the third edition of Thomas Chippendale’s The Gentleman and Cabinet-Maker’s Director (1762). Elizabeth Derby West owned one of the most elaborate Salem sofas (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston), whereas her relatives, John and Elizabeth West Gardner, purchased a slightly less ornate example for their new home in 1805 (fig. 35). Both sofas have a molded crest rail and a carved center ornament and arms. In 1801, Samuel McIntire charged Jacob Sanderson "1.7.0" for "carving [a] Sofa and working the top rail."[46]
As the last entry indicates, sofas "without [a] mahogany top" were also fashionable. In 1799, Salem upholsterer William Lemon shipped "two Mahogany sofas stuVed in Russia Sheetg [with] Copperplate furniture covers fring’d and bound" on the ship John bound for Surinam. While receipts show that the Sanderson firm made sofas in the 1790s, probably for local clients, sofas do not appear on their surviving shipping invoices until 1805. In April, Elijah Sanderson sent six sofas valued at one hundred dollars each on the ship Exeter.[47]
[50] EASY CHAIR FRAME———7
Making———2.50
[in ink] Voted June 1st 1802———6
[Making]———2.50
Although no easy chair has been documented to a specific Salem cabinetmaker or chair maker, an example that descended in the George Rea Curwen family (fig. 36) was probably made there about 1800. The contours of the cheeks and crest are similar to those in Hepplewhite’s design for a "Saddle Check, or easy chair" (fig. 37). References to easy chairs are rare in shipping manifests, suggesting that most were commissioned by local consumers. Merchant Aaron Waite’s large order for furniture from the Sandersons in 1796 included "1 Easy chair stuft" valued at twelve dollars. Five years later, upholsterer Jonathan Bright charged $8.50 for "Stuffing" an easy chair.[48]
[51] MAHOGANY CHAIR, finished with drapery back, &c. excluding the carving———6
Making———2
[in ink] Voted December 1st 1801———5.50
[Making]———2
This entry probably refers to a high-back upholstered armchair with a carved crest. Several examples from Salem are known, including a matching pair in the Winterthur Museum and the one illustrated in figure 38. The term "drapery back" refers to the carved swag on the crest rail. The shape of the crest was adapted from a sofa design on plate 35 in Sheraton’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Drawing Book, and the sloping arms and turned supports were derived from the chair shown on plate 6, number 3, of The London Chair-Makers’ and Carvers’ Book of Prices (1802).[49]
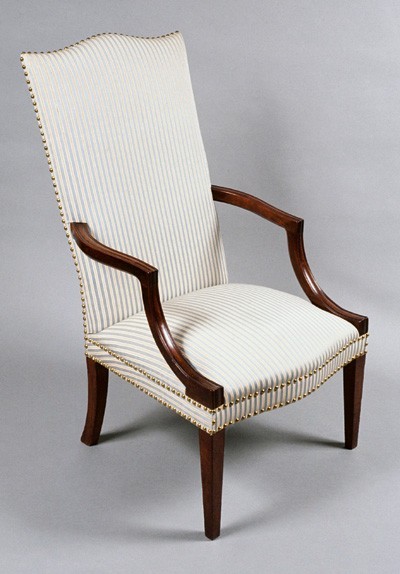
[52] LOLLING-CHAIR FRAME, with mahogany arms———5
Making———2
Inventories attest to the popularity of lolling chairs in Salem and indicate that most were used in parlors in pairs. Many of those shipped as venture cargo had muslin upholstery and slipcovers. Upholsterer William Lemon sent four mahogany lolling chairs "with copperplate furniture covers, Fring’d and bound with cotton lace" valued at twenty dollars each on the ship John bound for Surinam in 1799. No lolling chair can be documented to a specific Salem maker, but many have local histories. A chair that descended from John and Elizabeth Gardner (fig. 39), the original owners of the Gardner-Pingree House, represents one of the most popular designs. The couple purchased several pieces of furniture for their new house from cabinetmaker Nathaniel Safford in 1805.[50]
[53] WINDOW-STOOL FRAME, excluding the carving———6
Making———2
Many mahogany window stools are attributed to Salem, including a set of four that remain in their original location in the parlor of the Peirce-Nichols House (fig. 40). The carved details have parallels in Hepplewhite’s designs (fig. 41) and echoed features in the room, which was remodeled under the direction of Samuel McIntire in 1801. Hepplewhite commented that "the size of the window stools must be regulated by the size of the place where they are to stand." This may explain why the form does not appear on any venture cargo lists.[51]
[54] BEDSTEAD, mahogany, swelled pillars, excluding the carving, fluting and sacking, 16
Making (to be finished, the sacking put in, &c.)———4
[55] Ditto, birch, excluding the sacking———12
Making (finished as above)———4
[56] Ditto, mahogany field, excluding the sacking, 18
Making (finished as above)———4.50
[in ink] Dec 6th 1803 if all the parts mahogany $20
[57] Ditto, birch field, excluding the sacking, 12
Making (finished as above) 4.50
[in ink] Dec 6 1803———14
[58] Ditto, press———6
Making———2.50
[in ink] Voted Dec 1st 1801———5
[Making]———2.50
[59] Ditto, cot, excluding the sacking———3
Making———1.50
[60] Ditto, low post———3
[in ink] Dec 6th 1803———3.50
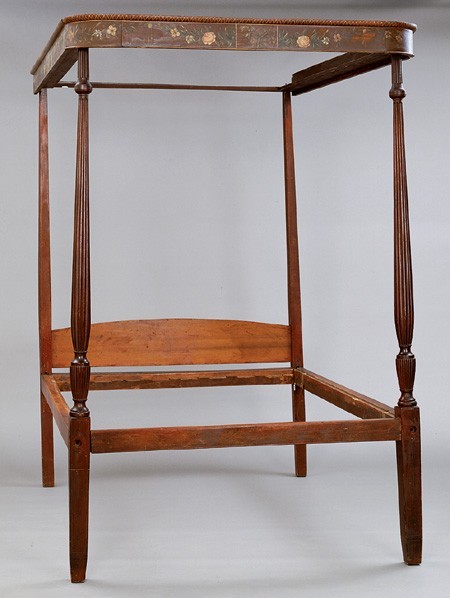
During the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, Daniel Clarke, Jonathan Gavet, and Nathaniel Safford invoiced the Sandersons for turning pillars for high- and low-post beds and urns for field beds. On October 7, 1800, Nathaniel Safford received three dollars for "two set[s] of highbedstead pillars." The Sandersons subcontracted most of the carving on bedsteads and other forms to Samuel McIntire. Two of the most ornate posts attributed to McIntire’s shop are on a bedstead made for Jerathamiel Peirce (fig. 42). A bedstead originally owned by George and Elizabeth Watson is less elaborate, but more typical of Salem production (fig. 43). Family tradition maintains that it survived a fire at their house in 1801. The bed retains its original painted cornice with floral and leaf swags, tassels, and central landscape panels in shades of brown, orange, yellow, and pink. On June 5, 1804, Samuel Page paid Jacob Sanderson six dollars for a "bedcornish & Painting same." Bed cornices are often mentioned in the accounts of fancy chair makers. Richard Austin received $4.50 for "Painting & Gilding [a] set [of] Cornishes" for Mrs. Rodgers’ bed in October 1805.[52]
Cots were the least expensive sleeping form listed in the price book. In 1804, Joshua Howard made one for Capt. Andrew Tucker, charging $1.75 for the frame, two dollars for labor, and six dollars for "10 yds Russia Duck." Six years later, Frederick Breed paid Jacob Sanderson’s estate $3.50 for "a Cott bedsted" and an additional $3.50 for the canvas bottom. A nineteenth-century folding cot found in the attic of the Gardner-Pingree House in Salem (fig. 44) consists of two chamfered square rails supported by two sets of crossed legs with stretchers. The joints are marked with Roman numerals and secured with wooden pegs. The position of the legs is adjustable using either of two holes at the center of the legs and a removable peg. The end of each rail is bound with a narrow metal band next to which is a half-inch round hole presumably to secure a frame for curtains or a canopy. The sleeping platform consists of two pieces of coarse canvas sewn together down the middle with each outer edge permanently embedded into the rail using glue and a wedge of wood. A French engraving from about 1818 shows a cot of similar construction being used in a garret chamber (fig. 45).[53]
[61] SEAMAN’S CHEST, 4 feet, without
painting, 6
Making———2
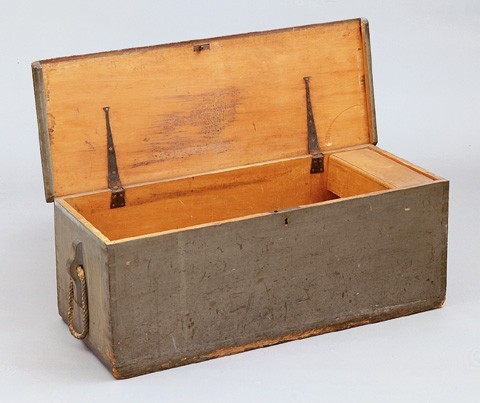
Several seaman’s chests from Salem are known, most of which are comprised of six boards and have massive corner dovetails and a hinged lid. The chest owned by Captain Charles Hoffman of Salem (fig. 46) has the traditional rope beckets on either side for carrying. The plain unpainted interior has a narrow covered till to one side. Other examples have additional features such as a small drawer below or partitions to secure bottles.
[in ink] Voted Dec 6th 1803
That the price of the large size
[62] Mehogany Coffin be———$20
[63] Cedar Ditto———14
[64] Pine ditto———4
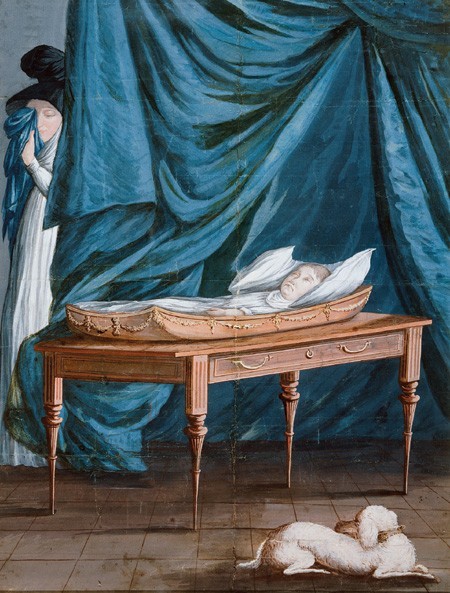
The Sanderson firm was probably producing coffins by 1789, when they imported fifty-three cedar logs from Charleston, South Carolina. Salem cabinetmakers preferred that wood for coffins, the interiors of small drawers, and cradles. Thomas Hodgkins’ account with the firm mentions only three coffins between July and December 1808. In August and November, he made pine coffins for two dollars each. References to coffins in business papers often give the name of the deceased or an agent of their estate. Decorative painter Robert Cowan charged the Sandersons $3.33 1/3 for a "Coffin Plate Lettered & Clasp for Mrs. Dana" in 1803, and Hodgkins’ account mentions a "coffin for Mr. Clark" in July 1808. Although coffins for children are not specifically mentioned in the price book, they were undoubtedly less expensive than comparable examples for adults. Michele Felice Cornè’s The Death of William depicts a child’s example commissioned by the Webb or Luscomb family of Salem (fig. 47).[54]
The clerk of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society made the last notations in the price book on December 6, 1803. Earlier that year, nine members had joined forces to send fifty cases of mahogany furniture valued at over $5,000 to Brazil. Although this venture was consistent with the society’s mission to create "important advantages" for its members, Elijah Sanderson’s instructions to supercargo Jeremiah Briggs suggests that external and internal forces were undermining the price agreement:
It often happen that furniture shipped by different people on board the same vessel is invoiced at different prices some higher and some lower of the same kind and quality and sometimes there is a difference in the goodness of the work and stock and when the whole is sold together at a particular rate for the invoice and all of the different invoices together, it is a disadvantage to those whose furniture put a lower rate is of a quality to have it sold together—therefore I wish you to sell mine by itself—not to mix it in a bargin with others and let me have the benefit of the sale of my own—you will find that my furniture is all marked with a brand E.S. on the back of each piece besides the mark on the case.
Given the competitive and entrepreneurial nature of Salem’s cabinetmaking trade, it was inevitable that competition with non-members would arise.[55]
The Sandersons’ business began to unravel following Jacob’s death in 1810 and ended amid bitter lawsuits when the restructuring failed. The furniture industry had suffered during the embargo of 1807 and the War of 1812. During this period, many cabinet and chair makers went bankrupt, and the furniture export trade all but vanished. In 1811, Rev. William Bentley admonished artisans involved in speculative ventures, many of whom had joined new religious organizations that challenged the supremacy of older established churches in town:
A strange deficiency of honesty among the officers of the Churches which have professed great zeal for conversions. Deacons S[anderson, Elijah] and L[amson] are added to the list of fraudulent bankrupts, & B[urpee] A[mes] is abroad upon the public courtesy....Salem has been unhappy in the wretches designated for these oYces....The failures of the speculators have strongly fallen upon the enthusiastic leaders of little Sects. Deacons Batchelder, Saunderson, Meservy, Safford, Adams, Palfrey, Lamson....None of these have been natives of Salem or well informed men, but thrusting themselves from mechanic employment’s into mercantile affairs & venturing largely upon credit, breaking embargo laws, & and making promises have plunged themselves into the greatest evils.[56]
For many members of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, economic misfortune extracted a much larger toll. In 1810, Eziekiel Goodnow and George Martin died at the early ages of thirty-six and thirty-nine respectively. The following year, Edmund Johnson was lost at sea while overseeing his own declining business. Samuel Cheever committed suicide in 1818. Other members who had drifted into town during its prosperous days moved on and found opportunities elsewhere. Jonathan Marston, for example, settled in Maine in 1812 and became a lumber dealer. Salem’s furniture industry eventually recovered and expanded in the ensuing decades under the leadership of a new generation of artisans, who presumably had not been members of the earlier society. They found a new voice for their collective interests in the founding of the Salem Charitable Mechanic Association in 1817, electing cabinetmaker Thomas Needham as their first president.[57]
APPENDIX A
NEHEMIAH ADAMS was baptized in Ipswich, Massachusetts, on April 16, 1769, and died in Salem on January 24, 1840. He married Mehitable Torry of Boston in 1802. He purchased his shop on the corner of Newbury and Williams Streets in Salem in 1796. It burned down on April 3, 1798. Adams was briefly in partnership with Benjamin Adams and Thomas Russell Williams in 1804. The former was active in the venture cargo trade and was a part owner of three vessels, including the brig Unicorn in 1804 (with the Sandersons). Documented furniture includes a labeled gentleman's secretary (Winterthur Museum) and a suite of furniture made for Lucy Hill Foster in 1810.
Sources: Ethel Hall Bjerkoe, The Cabinetmakers of America (Garden City, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1957), p. 20; Henry Wyckoff Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1927), p. 23; Margaret Burke Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture" (master's thesis, University of Delaware, 1976), p. 140; Essex County Registry of Deeds, 159: 232; A. Frank Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, Massachusetts, 1789-1900 (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1906), pp. 62, 86, 191; Fiske Kimball, "Salem Furniture Makers II, Nehemiah Adams," Antiques 24, no. 6 (December 1933): 218-20; Charles Montgomery, American Furniture: The Federal Period (New York: Viking Press, 1966), no. 181; and Nancy Cooper, "Some Documented Salem Furniture," House Beautiful 69, no. 4 (April 1931): 280-81.
WILLIAM APPLETON was baptized in Ipswich, Massachusetts, on June 30, 1765, and died in Salem on September 23, 1822. He probably apprenticed with his father, William. The younger Appleton's shop was on Essex Street by 1794, and near the Sun Tavern on the corner of Liberty and Charter Streets from 1795 until 1804. He purchased a house and land on Market Street in 1798. He was a part owner of the snow Fanny with the Sandersons and the schooner Olive Branch with Josiah Austin and the Sandersons. Documented pieces include a lady's tambour desk (Winterthur Museum) and a labeled secretary-and-bookcase (Winterthur Museum).
Sources: Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 29; Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, p. 26; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 153-56; Essex County Registry of Deeds, 164: 172; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, pp. 59, 136; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," p. 154; and Montgomery, American Furniture, no. 178.
JOSIAH AUSTIN was born in Charlestown, Massachusetts, on April 27, 1746, the son of Josiah Austin (b. 1719) and Mary Austin. He died in Salem on November 5, 1825. His brother Richard was a chair maker. Josiah moved to Medford in 1775 and was in Salem by 1779 when he joined with the Sandersons to establish a cooperative furniture export business. He was a part owner of the schooner Olive Branch in 1796 with the Sandersons and William Appleton. Josiah was one of the surveyors of boards, plank, and timber for the town of Salem in 1799. In 1803, his son Josiah died at sea in the schooner Friendship that was owned by fellow society members. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Daniel Austin, Austin manuscript genealogy, Phillips Library, Peabody Essex Museum; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 32; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," p. 157; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, p. 136; and Brock Jobe and Myrna Kaye, New England Furniture, The Colonial Era: Selections from the Society for the Preservation of New England Antiquities (Boston, Mass.: Houghton Mifflin, 1984), p. 232.
RICHARD AUSTIN was baptized in Charlestown, Massachusetts, on July 1, 1744, the son of Josiah and Mary and brother of Josiah. He married Isabel Symonds in Salem in 1797 and died of consumption in Salem on April 20, 1826. He was primarily a chair maker. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Daniel Austin, Austin manuscript genealogy; Bjerkoe, The Cabinetmakers of America, p. 32; and Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 26.
SAMUEL BARNARD was born in Watertown, Massachusetts, on July 22, 1776, the son of Major Samuel Barnard and Elizabeth Bond. He died in Watertown on June 14, 1858. He was in Salem by May 30, 1799, when he married Elizabeth Cook. He was a part owner of the schooner Friendship in 1802 with Edmund Johnson, George W. Martin, and Jonathan Marston. Barnard shipped furniture in 1805 on the schooner Good Intent with other members of the society. A card table branded "S.B." (Yale University Art Gallery) has been attributed to him.
Sources: Benjamin Hewitt et al., The Work of Many Hands: Card Tables in America, 1790-1820 (New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Art Gallery, 1982), p. 136, no. 19; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, p. 67; David L. Barquist, American Tables and Looking Glasses in the Mabel Brady Garvan and Other Collections at Yale University (New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Art Gallery, 1992), pp. 188-91.
SAMUEL CHEEVER was born in Manchester, Massachusetts, on March 12, 1756. He was the son of the Reverend Ames Cheever, the town's minister, and his fourth wife, Sarah Davis. Samuel hung himself on May 14, 1818, and left an estate valued at $1,420.80. He was in Salem by March 29, 1787, when he married Anna Ropes (d. 1799). He took his second wife Hannah Clark on May 10, 1800. Samuel purchased his shop at the end of Court Street from cabinetmaker and merchant Henry Rust in 1796. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 62; Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 33; John T. Hassam, Ezekiel Cheever and Some of His Descendants (Boston: David Clapp and Son, 1879), pp. 36-37; and Essex County Registry of Deeds, 159: 268.
DANIEL CLARKE was born in Braintree, Massachusetts, on March 14, 1768, and died in Salem on March 30, 1830. He was the son of Captain Peter Clarke and Hannah Clarke. In October 1794, he moved from Boston to work for the Sandersons for whom he did carving, turning, and cabinetmaking. Clarke established his own shop on Essex Street opposite Cambridge Street in 1796. On February 11, 1800, he moved to Chestnut Street near Summer and Norman Streets. He married Mary Sanderson in 1803. A sideboard made by him for Nathaniel Ropes in 1797 is in the Ropes Mansion (Peabody Essex Museum).
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 33; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 65; and Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," p. 161.
EZEKIEL GOODNOW was born in Princeton, Massachusetts, on October 27, 1774. He married Sophia Farrington in Salem on December 20, 1801, and died before December 25, 1810, when his wife advertised for the administration of his estate. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 43.
WILLIAM HOOK was born in Salisbury, Massachusetts, on February 19, 1777, and died in Roxbury, Massachusetts, on May 15, 1867. He was apprenticed at the age of fourteen to John Swett in Salisbury. He came to Salem in 1796 and worked for Edmund Johnson for two years and then the Sandersons for one year before opening his own shop at Essex and Court Streets in 1800. He married Abigail Greenleaf in 1800. He moved his shop to Federal Street in 1803, to Marlborough Street in 1804, and to Essex Street in 1818. Documented pieces include furniture made for his sister in 1809 (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston), a chest of drawers and dressing glass made in 1818 (Peabody Essex Museum), and a suite of furniture made for Capt. George Hodges in 1819. Hook's business papers are in the Phillips Library of the Peabody Essex Museum.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 48; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, pp. 128-29; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 169-83; Fiske Kimball, "Salem Furniture Makers III, William Hook," Antiques 25, no. 4 (April 1934): 144-46; Richard H. Randall, Jr., American Furniture in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston (Boston: by the museum, 1965), nos. 37, 49, 99, 101; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 177-82.
EDMUND JOHNSON was the son of Edward Johnson (1722-1799) a Lynn, Massachusetts, "shop joiner." He died at sea before July 19, 1811. He was in Salem by 1793 when he married the widow Betsy Smith. He purchased property on Federal Street at Bickford from the estate of cordwainer John Bullock in 1798. He had a shop at River and Federal Streets in 1796 and subsequently moved to Essex Street. Very active in the export trade, he was a part owner of the schooner Friendship with George W. Martin, Jonathan Marston, and Samuel Barnard in 1802 and a half owner of the schooner Theoda in 1803. Labeled pieces by Johnson include a gentleman's secretary (Winterthur Museum), a slant top desk (Peabody Essex Museum), a lady's tambour desk, a sideboard, a tambour desk, and a pair of knife boxes.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 50; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 135; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 184-91; Essex County Registry of Deeds, 165:19; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, pp. 67, 183; Montgomery, American Furniture, no. 179; Dean A. Fales, Jr., Essex County Furniture: Documented Treasures from Local Collections, 1660-1860 (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1965), nos. 22-23; Winterthur Museum Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, 71.3513; Antiques 65, no. 6 (June 1954): 466-68; Fales, Essex County Furniture, nos. 20, 21.
JONATHAN MARSTON was born in Hampton, New Hampshire, on May 13, 1777, the son of farmer Elisha Marston. Jonathan died in Machiasport, Maine, on March 12, 1862. He married Sarah Holt in Salem on July 5, 1801. The following year he was a part owner of the schooner Friendship with Edmund Johnson, George W. Martin, and Samuel Barnard. His brother Morrill Marston (1785-1831) was in business in Salem around 1805. Jonathan moved to Machiasport about 1812 where he kept a store and engaged in the lumber business with his brother Elisha. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, p. 67; Nathan W. Marston, The Marston Genealogy in Two Parts (South Lubec, Maine: by the author, 1888), pp. 143-44.
GEORGE WHITEFIELD MARTIN was born on March 5, 1771, in Marblehead, Massachusetts, and died in Salem on January 5, 1810. He was in partnership with Robert Choate (b. 1770) in Concord, New Hampshire, from 1794 to 1796. Martin moved to Salem by April 11, 1797, when he married Sally Bullock. Through his wife's family he acquired land and a shop on Federal Street next to Edmund Johnson. In 1802, Martin was a part owner of the schooner Friendship with Edmund Johnson, Samuel Barnard, and Jonathan Marston. His tools and shop on Federal Street were sold at auction on June 19, 1810. A card table with the label of Choate and Martin (New Hampshire Historical Society) is the only documented piece by him.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 58; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 150; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 198-99; Hewitt et al., Work of Many Hands, p. 118; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, p. 67; Hewitt et al., Work of Many Hands, no. 3.
FRANCIS PULCIFER was born in 1771 (possibly in Ipswich, Massachusetts) and died on June 24, 1823, in Salem. He married four times: Hannah Trask (1792), Martha Hodgkins (1806), Hannah Haskell (1814), and Lydia Lakeman (1816). Pulcifer was in business with Samuel Frothingham on Church Street until he moved to Court Street in 1795 when the partnership dissolved. Four years later, he purchased property on Williams Street from watchmaker James Dalrymple. Pulcifer was active in the venture cargo trade. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 65; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 180; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 213-14; Essex County Registry of Deeds, 165: 183.
ELIJAH SANDERSON was born in Watertown, Massachusetts, on October 10, 1751, and died in Salem on February 18, 1825. In 1781, he married Mary Mulliken whose brother Samuel was a clockmaker. With his brother Jacob and Josiah Austin, Elijah started a cooperative furniture export business in 1779. Their firm employed many of the town's cabinetmakers, journeymen, turners, carvers, gilders, and upholsterers. The partners owned the schooner Olive Branch with William Appleton in 1796, the snow Fanny with Appleton in 1799, and the brig Unicorn with Nehemiah Adams in 1804. Documented furniture by him includes a desk-and-bookcase branded "ES," a slant-top desk (New England Historic Genealogical Society), a night table, a branded lady's tambour desk, a labeled (with Jacob Sanderson) desk-and-bookcase (Diplomatic Reception Rooms, U.S. Department of State), a card table (with Jacob Sanderson) with painted initials (Winterthur Museum), and a labeled (with Jacob Sanderson) pembroke table (Winterthur Museum). His business papers are in the Phillips Library of the Peabody Essex Museum.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 68; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, pp. 189-90; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 216-20; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, pp. 59, 136, 191; Mabel M. Swan, Samuel McIntire, Carver and the Sandersons, Early Salem Cabinetmakers (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1934); Winterthur Museum Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, 88.472; Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, opposite p. 32; Fales, Essex County Furniture, no. 37; Winterthur Museum Decorative Arts Photographic Collection, 70.279; Clement E. Conger and Alexandra W. Rollins, Treasures of State: Fine and Decorative Arts in the Diplomatic Reception Rooms of the U.S. Department of State (New York: Harry N. Abrams, 1991), no. 121; Montgomery, American Furniture, nos. 300, 322.
JACOB SANDERSON was born about October 20, 1757, in Watertown, Massachusetts, and married Katherine Harrington of Watertown in 1781. He died in Salem in December of 1810. In partnership with his brother Elijah, he was a part owner of three vessels (see above). Documented furniture by him includes a bed cornice (Peabody Essex Museum), two tables (Winterthur Museum), and pieces jointly labeled with Elijah Sanderson (see above). His business papers are in the Phillips Library of the Peabody Essex Museum.
Sources: Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts, p. 68; Bjerkoe, Cabinetmakers of America, p. 190; Clunie, "Salem Federal Furniture," pp. 220-26; Hitchings, Ship Registers of the District of Salem and Beverly, pp. 59, 136, 191; Margaret Burke Clunie, Anne Farnam, and Robert Trent, Furniture at the Essex Institute (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1980), no. 34. Montgomery, American Furniture, nos. 300, 301.
ROBERT WALLIS was born about 1764 and died in Salem on October 2, 1824. He married Mary Polly Aveson in the town on December 13, 1787. The following year, he purchased land and buildings on Essex Street from the estate of Mary Ford. No documented furniture by him is known.
Sources: Vital Records of Salem, Massachusetts, 4: 430, 6: 302; Essex County Registry of Deeds, 147: 275.
APPENDIX B
Salem Cabinetmakers' Price Book
(fig. 48-67)
Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” p. 302. Although Edmund Johnson was primarily a cabinetmaker, he occasionally sold chairs. In the October 31, 1800, Salem Gazette, he advertised “mahogany furniture, and Windsor Chairs of all kinds at the lowest cash prices.” For more on Windsor chair makers in Salem, see Nancy Goyne Evans, American Windsor Chairs (New York: Hudson Hills Press, 1996), pp. 365–69. Mabel Munson Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons: Early Salem Cabinet Makers (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1934), p. 29. Some cabinetmakers, such as Daniel Clarke, advertised cabinetmaking, chair making, and carving.
Richard J. Morris, “Wealth Distribution in Salem, Massachusetts, 1759–1799, the Impact of the Revolution and Independence,” Essex Institute Historical Collections 114 (1978): 101; and James Duncan Phillips, Salem and the Indies: The Story of the Great Commerical Era of the City (Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1947), pp. 224–30. Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” p. 14.
Fiske Kimball, Samuel McIntire, Carver: The Architect of Salem (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1940), p. 71. The Diary of William Bentley, D.D., Pastor of the East Church, Salem, Massachusetts, 4 vols. (1905–1914; reprint, Gloucester, Mass.: Peter Smith, 1962), 4: 55. Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” p. 300.
Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, pp. 1–3. The Sandersons were originally from Watertown, and Austin was originally from Charlestown. Austin’s association with the Sandersons may explain his brother Richard’s membership in the Cabinet-Maker Society. Richard Austin was primarily a chair maker, and membership was generally limited to master cabinetmakers.
Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” p. 23. See also Margaret B. Clunie, “Furniture Craftsmen of Salem, Massachusetts in the Federal Period,” Essex Institute Historical Collections 113 (1997): 191–203.
See the appendix for biographical information on the founding members. In the initial printing, the name of Edmund Johnson was left off the list, probably in error, so the printer pasted a new list in a slightly different order over the original listing. Daniel Clarke, who served as first clerk of the Salem Cabinet-Maker Society, worked as a cabinetmaker and carver in Boston prior to 1794 and as a journeyman for the Sandersons in 1794. The Sandersons purchased ebony from William Appleton in 1799. Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” pp. 29, 30, 48.
Jenks advertised copies of the ?rst edition of Hepplewhite’s The Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Guide (1788) in 1791 and 1792. The copy he advertised in 1794 could be the first or second (1789) edition. For more on these copies and the importation of design books into Salem, see Barbara Jobe, “Importation of Books into Salem, Massachusetts: 1783–1799,” unpublished research paper, 1972, p. 5, PL, PEM. Jacob Sanderson’s 1810 inventory lists three copies of Hepplewhite’s design book (Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, p. 55).
Clunie, “Salem Federal Furniture,” p. 302. Clunie notes that the 109 surviving manifests are incomplete for the period mentioned, thus her analysis only points to the relative popularity of each form. Her list includes the following forms and number of references to each: basin stands (3), bureaus (23), cabinets (3), cabinet-bookcases (2), candlestands (2), card tables (39), clock cases (9), chairs (1,231), chests (6), desks (177), desk and bookcases (1), lady’s secretaries (6), light stands (4), lolling chairs (10), night tables (1), pembroke tables (7), secretaries (6), secretary-bookcases (19), sideboards (8), sofas (4), stands (25), and tables (80). Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, p. 19. A work table made by Philadelphia cabinetmaker Robert McGuffin in 1808 is illustrated and discussed in David L. Barquist, American Tables and Looking Glasses in the Mabel Brady Garvan and Other Collections at Yale University (New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1992), pp. 290–93. An invoice dated November 21, 1809, for furniture shipped by Elijah Sanderson on the schooner Neutrality includes three lady’s dressing boxes valued at six dollars each. Sanderson Papers, (hereafter cited SP), PL, PEM. Imported knife boxes, tea caddys, trays, and bottle boxes were readily available in Salem. American cabinetmakers usually found it more profitable to sell British examples than to produce their own interpretations.
Checkered cock beading occurs on several elaborate case pieces made in Salem during the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. See Jonathan Fairbanks and Elizabeth Bates, American Furniture, 1620 to the Present (New York: Richard Marek Publishers, 1981), p. 199, for a magnificent chest-on-chest with checkered cock beading made for Elizabeth Derby West in 1796.
Richard H. Randall, Jr., American Furniture in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston (Boston: By the museum, 1965), p. 96, fig. 67.
Theodore R. Crom, “An American Beauty: The Samuel Mulliken II, Salem, Mass., Dwarf Clock,” National Association of Watch and Clock Collectors Bulletin 37, no. 299 (December 1995): 756–61. Other members of the Mulliken family had connections in Salem. Samuel’s brother Joseph worked as a watchmaker there in the early 1790s, and his brother, John, sent two clocks as venture cargo with the Sandersons in 1799 (Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, pp. 2, 8, 14). Benjamin Balch, a member of the Newburyport clockmaking family, began working as a watchmaker in Salem in 1796. Edmund Currier is documented as a clockmaker in David R. Proper, “Edmund Currier Clockmaker,” Essex Institute Historical Collections 91, no. 4 (October 1965): 281–88. Henry Wyckoff Belknap, Artists and Craftsmen of Essex County, Massachusetts (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1927), pp. 84–108.
Elijah Sanderson made a lady’s secretary similar to the one shown in fig. 19 for his daughter Sally. A photograph of the piece is in the Sanderson Papers, PL, PEM. Montgomery, American Furniture, no. 190.
Conger and Rollins, Treasures of State, p. 179; and Brock Jobe, et al., Portsmouth Furniture: Masterworks from the New Hampshire Seacoast (Hanover, N.H.: University Press of New England for the Society for the Preservation of New England Antiquities, 1993), p. 108. Christie’s, The Collection of Mr. and Mrs. James L. Britton, New York, January 16, 1999, lot 605. The chest with the modest cant is illustrated in Bivins, “The Convergence and Divergence of Three Stylistic Traditions,” p. 88, fig. 34. Another example is published in Israel Sack, Inc., American Furniture from Israel Sack Collection 3 (January 1970): 580, no. 1353. Related examples from other centers influenced by Salem include a chest by Langley Boardman discussed in Jobe, Portsmouth Furniture, p. 106.The Needham chest appears in Dean A. Fales, Jr., Essex County Furniture: Documented Treasures from Local Collections, 1660–1860 (Salem, Mass.: Essex Institute, 1965), fig. 28. The Waite receipt is cited in Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, p. 36.
A set of three tables (ca. 1800), probably from the Portsmouth-Salem area, is in the Strawbery Banke collection. Each section has tapered legs with simple inlay. The dimensions are close to those given in the first table entry in the price book. For an illustration of the set, see Northeast Auctions, New Hampshire Auction, Portsmouth, N. H., November 6–7, 1999, lot 857. Invoices dated January 18, 1802, and December 25, 1809, SP, PL, PEM.
Ibid.
Ledger of William Gray, 1750–1819, PL, PEM.
Examples appear in Skinner’s, American Furniture and Decorative Arts, Bolton, Massachusetts, August 12, 2000, lots 57, 64, 328.
Israel Sack, Inc., American Furniture from Israel Sack Collection 2 (April 1965): 305, no. 744. Randall, American Furniture in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, no. 108; Conger and Rollins, Treasures of State, p. 206; and Montgomery, American Furniture, p. 389. Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, pp. 19, 31.
For related fire screens, see Dean A. Fales, Jr., Furniture of Historic Deerfield (New York: E. P. Dutton, 1976), p. 163; and Montgomery, American Furniture, no. 203. The Gavet stand is pictured in Randall, American Furniture in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, no. 106.
Receipt, William Appleton to Lydia Waite, March 1796, Waite Family Papers, PL, PEM. Invoice for the schooner Sally, March 30, 1802, SP, PL, PEM. Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, p. 31.
Although square-back sofas with turned legs are illustrated in Thomas Sheraton’s Cabinet-Maker and Upholsterer’s Drawing Book (1793), the form did not become popular in Salem until around 1810. In that year, Lucy Hill purchased a fully carved version from Nehemiah Adams for sixty-seven dollars. Upholsterer Jonathan Bright charged her nineteen dollars for “Stufing” it and an additional twelve dollars for making a cushion (Nancy Cooper, “Samuel McIntire, Carver; Nehemiah Adams, Maker,” House Beautiful 69 [1931]: 394–95). Shipping manifest, April 25, 1805, SP, PL, PEM.
Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, pp. 31, 37. Two other documented Salem bedsteads are at the Peabody Essex Museum. One was made by Jacob Sanderson for Aaron Waite in 1807 (Clunie, Farnam, and Trent, Furniture at the Essex Institute, p. 38). The other, which bears the label of Thomas Needham, is illustrated in Fales, Essex County Furniture, no. 27. A Salem field bed, 1801–1810, is pictured in Sotheby’s, Important Americana, Furniture, Folk Art and Decorations, New York, October 15, 1999, lot 83; and Northeast Auctions, New Hampshire Weekend Americana Auction, Portsmouth, N. H., March 3–4, 2001, lot 949. Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, p. 28.
Swan, Samuel McIntire and the Sandersons, pp. 6, 22–23. Mark Pitman charged twenty dollars for a mahogany coffin and five dollars for a silver plate for “Miss Abigail Ropes” in 1839 (Nathaniel Ropes Papers, PL, PEM). Salem cabinetmakers do not appear to have exported coffins.
